
Research Article
Discovery of a Highly Selective Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand,
1-(4-(6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2
(1H)-yl)butyl)-3-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (CM398),
with Drug-Like Properties and Antinociceptive Effects In Vivo
Sebastiano Intagliata,
1
Abhisheak Sharma,
2
Tamara I. King,
2
Christophe Mesangeau,
3
Michael Seminerio,
4
Frederick T. Chin,
5
Lisa L. Wilson,
6
Rae R. Matsumoto,
4,7
Jay P. McLaughlin,
6
Bonnie A. Avery,
2
and Christopher R. McCurdy
1,3,8
Received 1 May 2020; accepted 16 June 2020
Abstract.
The sigma-2 receptor has been cloned and identified as Tmem97, which is a
transmembrane protein involved in intracellular Ca
2+
regulation and cholesterol homeostasis.
Since its discovery, the sigma-2 receptor has been an extremely controversial target, and
many efforts have been made to elucidate the functional role of this receptor during
physiological and pathological conditions. Recently, this receptor has been proposed as a
potential target to treat neuropathic pain due to the ability of sigma-2 receptor agonists to
relieve mechanical hyperalgesia in mice model of chronic pain. In the present work, we
developed a highly selective sigma-2 receptor ligand (sigma-1/sigma-2 selectivity ratio >
1000), 1-(4-(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)butyl)-3-methyl-1H-
benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (CM398), with an encouraging in vitro and in vivo pharmaco-
logical profile in rodents. In particular, radioligand binding studies demonstrated that CM398
had preferential affinity for sigma-2 receptor compared with sigma-1 receptor and at least
four other neurotransmitter receptors sites, including the norepinephrine transporter.
Following oral administration, CM398 showed rapid absorption and peak plasma concentra-
tion (Cmax) occurred within 10 min of dosing. Moreover, the compound showed adequate,
absolute oral bioavailability of 29.0%. Finally, CM398 showed promising anti-inflammatory
analgesic effects in the formalin model of inflammatory pain in mice. The results collected in
this study provide more evidence that selective sigma-2 receptor ligands can be useful tools in
the development of novel pain therapeutics and altogether, these data suggest that CM398 is
a suitable lead candidate for further evaluation.
KEY WORDS: sigma receptors; sigma-2 receptor; neuropathic pain; formalin assay; pharmacokinetic.
INTRODUCTION
Neuropathic pain is a major clinical problem that results
in a drastic reduction to the quality of life in patients who are
affected with this chronic condition (1,2). It represents one of
the most frequent causes of adult disability and a consider-
able health-care cost which consists of medical expenses and
lost workdays. It has been estimated that approximately 20
million individuals in the USA suffer from some form of
peripheral neuropathy (3). The most common reasons of
developing peripheral neuropathy include physical injury
(trauma), chronic diseases (diabetic neuropathy), and expo-
sure to toxins (3). Despite the fact that neuropathic pain is a
common medical problem, there are only a few effective
treatment options, each with their own limitations, thus the
management of chronic pain is quite complicated and
challenging. First-line treatments include antid epressant
1
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, Univer-
sity of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32610, USA.
2
Department of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy, University of
Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32610, USA.
3
Department of BioMolecular Sciences, School of Pharmacy, The
University of Mississippi, University, Mississippi 38677, USA.
4
Department of Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences, West Virginia
University, Morgantown, West Virginia 26506, USA.
5
Department of Radiology, Stanford University School of Medicine,
Stanford, California 94305, USA.
6
Department of Pharmacodynamics, College of Pharmacy, University
of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32610, USA.
7
Present Address: Dean’sOffice, Touro University California College
of Pharmacy, Vallejo, CA 94592, USA.
8
To whom correspondence should be addressed. (e–mail:
[email protected]fl.edu)
The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
DOI: 10.1208/s12248-020-00472-x
1550-7416/20/0000-0001/0
#
2020 American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists
agents such as tr icyclic antidepr essants (TCAs) and
serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or
anticonvulsant drugs such as calcium channel alpha-2-delta
ligands (gabapentinoids) (4). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs (NSAIDs) may be used for mild pain relief, whereas
narcotic agents are generally prescribed for pain that does not
respond to the first-line treatments (4). Although most of the
prescribed drugs are effective for alleviating pain symptoms,
they cause several side effects and possess notable liabilities
that include sedation, diplopia, and dizziness in case of
antiepileptic drugs (5), or tolerance, respiratory depression,
dependence, and addiction in case of opioids (6). Therefore,
there is a strong need for new therapeutics with fewer side
effects and increased effectiveness for pain management. To
this end, several new potential targets to treat neuropathic
pain have been proposed, and novel agents have shown
efficacy in preclinical models, and some have currently
reach ed investigation in clinical trials (7). Among these
approaches, sigma receptor ligands emerged as promising
tools for alleviating chronic pain (8). Sigma receptors are
transmembrane proteins present throughout the central
nervous system as well as in peripheral tissues (e.g., spleen,
liver, and kidney) (9). Two different receptor subtypes were
reported and identified as sigma-1 and sigma-2. The sigma-1
receptor was cloned over two decades ago, and the human
crystal structure has been reported (10,11), whereas purifica-
tion and cloning of the sigma-2 receptor have only recently
been published in 2017 (12). The sigma-2 receptor has been
confirmed as Tmem97 (transmembrane protein 97) (12).
Several literature reports suggest a role for the sigma-1
receptor in pain modulation, and either selective or non-
selective sigma-1 receptor ligands have shown antinociceptive
effects in animal models ( 13–16). In particular, the sigma-1
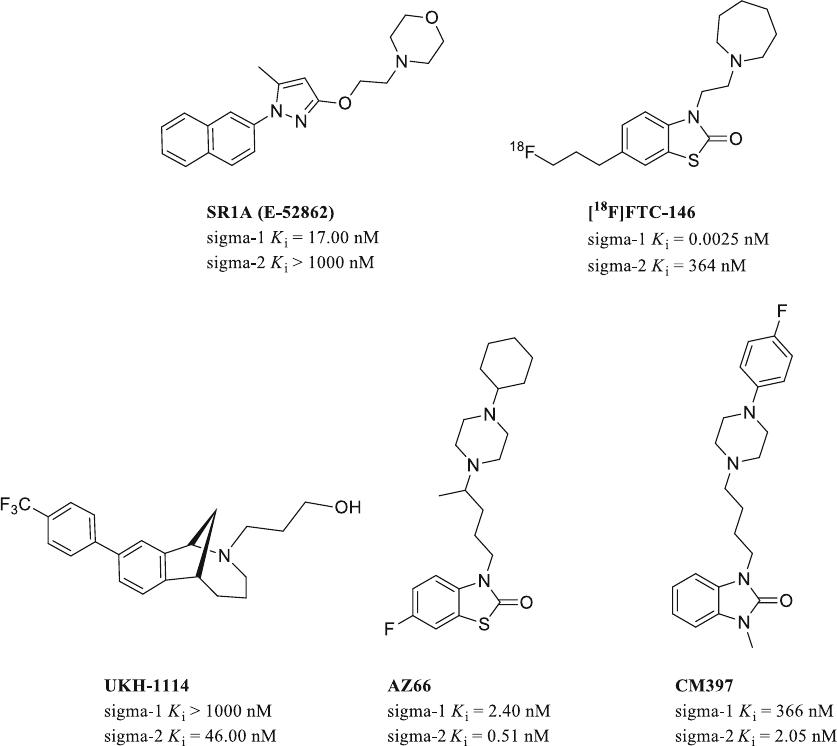
receptor antagonist S1RA (E-52862) (Fig. 1) has completed
successfully phase I clinical trials studies and is currently
under phase II investigation (17,18). Another example of
sigma-1 receptor antagonist is [
18
F]FTC-146 (Fig. 1) which
has entered into clinical trials as a positron emission
tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MRI)
diagnostic agent to pinpoint peripheral nerve injury (19–22).
Despite many years of research efforts focused on the
validation of the sigma-1 subtype as an effective target to
treat neuropathic pain (23), the evaluation of the sigma-2
receptor potential as a therapeutic target for pain target has
Fig. 1. Chemical structure and affinity values of selective sigma-1 antagonists S1RA (E-52862) and [
18
F]FTC-146 which
are current under clinical studies; selective sigma-2 agonist UKH-1114 and non- selective sigma-1/sigma-2 ligand AZ66
which have showed antineuropathic pain effects in mice; selective sigma-2 benzimidazolone-based analog CM397
94 Page 2 of 11 The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
also started to gain momentum. Most recently, the phenyl
methanobenzazocine derivative (UKH-1114, Fig. 1) as sigma-
2/Tmem97 agonist was reported to be able to produce
antinociceptive effects when administered IT to spared nerve
injury (SNI) mice, suggesting antineuropathic pain effects of
sigma-2 ligands (24). Moreover, the non-selective sigma-1/
sigma-2 ligand AZ66 (Fig. 1) demonstrated the ability to
alleviate multiple modalities of chronic pain with reduced
liabilities compared to opioids (16).
Our research group has been working for many years in
the development of selective sigma receptor ligands, including
benzimidazolone-based selective sigma-2 receptor li gands
(25,26). Several of our compounds have been used as
effective chemical probes in the elucidation of the putative
roles of the sigma receptor subtypes in many diseases such as
cancer, drug addiction, and pain (27–31). More recently, our
efforts have been focused on the translational research of
many of our lead molecules into effective diagnostic or
pharmacotherapies through a multi-disciplinary and inte-
grated approach. Herein, we report the synthesis, in vitro/in
vivo pharmacology evaluation, and preclinical pharmacoki-
netic studies of CM398, a highly selective sigma-2 receptor
ligand (sigma-1/sigma-2 selectivity ratio > 1,000), that demon-
strates anti-inflammatory analgesic effects in mice as an initial
proof-of-concept.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemistry
Reagents and starting materials were obtained from
commercial suppliers and were used without purification.
Precoated silica gel GF Uniplates from A naltech were used
for thin-layer chromatography (TLC). Column chromatog-
raphy was performed on silica gel 60 (Sorbent Technolo-
gies).
1
Hand
13
C NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker
APX400 (400 and 100 MHz, respectively) in CDCl
3
and
DMSO-d
6
solution. Chemical shift (δ) values are given in
parts per million ( ppm) using tetramethylsilane (TMS) and
DMSO or CHCl
3
as the internal standard; coupling
constants (J values) are given in hertz (Hz). For signal
multiplicities, the following abbreviations are used as
follows: s (singlet), d (doublet), dd (doublets of doublet),
ddd (doublet of doublet of doublets), t (triplet), br s (broad
singlet), and m (multiplet). The mass spectra (MS) w ere
recorded on a WATERS ACQUITY Ultra Performance LC
with ZQ detector in ES I or A PCI mode. The h igh
resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were recorded on a Waters
Micromass Q-TOF Micro m ass spectrometer w ith a lock
spray sourc e. Chemical names we re generated using
ChemDraw Ultra (CambridgeSoft, version 10.0).
N-Methyl-2-nitroaniline (2). A solution of 1-fluoro-2-
nitro-benzene (2.00 g, 14.17 mmol) in water (5 mL) was
added 40% aqueous methylamine ( 5 mL) at room temper-
ature, and the reaction mixture stirred at room temperature
under nitrogen. After 2 h, the reaction mixture was poured
into a sat urated aq ueous s olution of sodium chlo ride
(50 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The
organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate,
concentrated in va cuo, and the residue was puri fied by flash
column chromatography (hexane/ethyl acetate 9:1) to afford
2 as an orange oil (2.00 g, 93%).
1
H NMR (400 MHz,
DMSO-d
6
) δ 8.14 (d, J 0 5.5 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (dd, J 0 8.6,
1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (ddd, J 0 8.3, 6.9, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (dd, J 0
8.8, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 6.62 (ddd, J 0 8.3, 7.0, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (d,
J 0 5.0 Hz, 3H).
13
C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d
6
) δ 146.59,
137.19, 131.48, 126.72, 115.49, 114.80, 30.24. MS (ESI
+
) m/z
153 [M + H]
+
.
N
1
-Methylbenzene-1,2-d iamine (3). Asolutionof2
(2.00 g, 13.14 mmol) in methanol (20 mL) was added 10%
palladium on carbon (0.10 g) in a portion wise manner. After
addition and stirring for an additional 2 h under hydroge-
nated (H
2
) atmosphere at room temperature, the reaction
mixture was then filtered through a pad of celite, and the
filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to afford 3 as brown
residue, which was used in the next step without further
purification.
1
H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d
6
) δ 6.55 (t, J 0 7.3
Hz, 2H), 6.48–6.35 (m, 2H), 4.56 (d, J 0 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.42 (s,
2H), 2.70 (d, J 0 3.6 Hz, 3H).
13
C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d
6
)
δ 137.85, 135.75, 118.40, 117.37, 114.46, 109.78, 30.91. MS
(ESI
+
) m/z 123 [M + H]
+
.
1-Meth yl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (4). Amix-
ture of 3 (2.00 g, 16.40 mmol), 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole
(3.18 g, 19.60 mmol) in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (25 mL)
was stirred at 65°C for 5 h. The mixture was poured onto
water and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The
extract was washed with a saturated aqueous solution of
sodium chloride (35 mL) and dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate. The solvent was removed in vacuo, and the obtained
residue was crystallized from hexane-ethyl acetate (1:1) to
afford 4 as white crystals (1.90 g, 79%).
1
H NMR (400 MHz,
DMSO-d
6
) δ 10.82 (s, 1H), 7.06–6.93 (m, 4H), 3.25 (s, 3H).
13
C
NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d
6
) δ 155.07, 131.58, 128.85, 121.47,
121.13, 109.23, 108.21, 27.03. MS (ESI
+
) m/z 149 [M + H]
+
.
1-(4-Bromobutyl )-3-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2( 3H)-
one (5). K
2
CO
3
(0.56 g, 4.05 mmol) and 1,4-dibromobutane
(1.12 mL, 9.45 mmol) were added, under mechanical stirring,
to a solution of 4 (0.20 g, 1.35 mmol) in anhydrous DMF
(8 mL). The reaction mixture was heated at 60°C for 3 h.
After cooling, the mixture was poured into 100 mL of water,
extracted with eth yl acetate (3–40 mL), washed with a
saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, and dried
over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed in
vacuo, and the residue was purified by flash column
chromatography (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate 7:3) to afford
5 as a colorless oil (0.27 g, 70%).
1
H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3
)
d 7.06–7.03 (m, 2H), 6.96–6.91 (m, 2H), 3.88–3.86 (m, 2H),
3.41–3.38 (m, 2H), 3.63 (s, 3H), 1.89–1.85 (m, 4H).
13
C NMR
(101 MHz, CDCl
3
) d 154.41, 130.10, 129.17, 121.26, 121.23,
107.53, 107.50, 40.08, 33.13, 29.66, 27.15, 26.98. MS (ESI) m/z
305 [M + Na]
+
(
79
Br) and 307 [M + Na]
+
(
81
Br).
1-(4-(6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-
yl)butyl)-3-methyl-1H- benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one Hydro-
chloride (CM398). K
2
CO
3
(0.08 g, 0.62 mmol) and 6,7-
dimethoxy-1,2,3,4- tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrochloride
(0.05 g, 0.21 mmol) were added, under mechanical stirring,
to a solution of 5 (0.05 g, 0.18 mmol) in anhydrous DMF
(3 mL). The reaction mixture was heated at 40°C for 1 h.
94 Page 3 of 11
The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94

After cooling, the mixture was poured into 20 mL of water,
extracted with eth yl aceta te (3–30 mL), washed with a
saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, and dried
over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed in
vacuo, and the residue was purified by flash c olumn
chromatography (methylene chloride/methanol 95:5) to af-
ford 6, which was converted into the hydrochloride salt by
addition of HCl/dioxane and isolated as a white solid (0.026 g,
34%).
1
H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) d 11.26 (br s, 1H),
7.24–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.16–7.14 (m, 1H), 7.08–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.79
(s, 1H), 6.77 (s, 1H), 4.35–4.32 (m, 1H), 4.13–4.09 (m, 1H),
3.87 (t, J 0 7.2 Hz, 2H), 3.73–3.56 (m, 7H), 3.33–3.19 (m, 7H),
2.89–2.85 (m, 1H), 1.83–1.71 (m, 4H).
13
C NMR (101 MHz,
DMSO-d6) d 153.49, 148.16, 147.51, 129.57, 128.65, 123.23,
120.72, 119.77, 111.40, 109.65, 107.64, 107.60, 55.47, 55.41,
54.22, 50.99, 48.51, 39.65, 26.77, 25.11, 24.14, 20.49. HRMS
calcd for C
23
H
30
N
3
O
3
[M + H]
+
396.2287, found 396.2268.
Competition Binding Assays
Radioligand binding studies at sigma and non-sigma
receptors were performed using competition binding assays
in homogenates of rat brain tissues and following previously
reported procedures (26,32). Specific information regarding
tissues, radioligands, and drugs used in the assays are
reported in Table I.
Metabolic Stability in Rat Liver Microsomes
Phase-I metabolism stability of CM398 was studied in rat
liver microsomes. The incubation mixture consisted of liver
microsomal protein (1 mg/mL), CM398 (1 μM), phosphate
buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4), and reduced nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH, 2 mM). Verapamil (1 μM)
was used as a positive control to assess the metabolizing
capacity of rat liver microsomes. NADPH deficient micro-
somal reaction was performed as a negative control to reveal
the non-NADPH-dependent degradation, non-specific
binding, and chemical instability of the compound in the
reaction mixture. In a 96-well plate, 178 μL of buffer, 2 μLof
CM398/verapamil stock solution (100 μM), and 10 μL of liver
microsomes (protein 20 mg/mL) were added and equilibrated
for 5 min in a shaking water bath at 37°C. Total organic
content in reaction mixture was 1%. The reaction was started
by adding 10 μL of NADPH (40 mM). For the negative
control reaction, volume of NADPH was replaced by
phosphate buffer. An aliquot (20 μL) from the incubation
mixture was quenched at 0, 5, 10, 15, 30, and 45 min with
80 μL of ice cold acetonitrile containing internal standard (IS)
to terminate the microsomal reaction. The samples were
centrifuged at 4°C for 15 min at 12,000 rpm, and supernatants
were analyzed using U PLC/MS-MS for residual CM398
content. The positive and negative controls were also
processed similarly. The area under the curve (AUC) was
calculated for the analyte and IS in MassLynx, and the ratio
of the analyte to IS AUC was used to plot re lative
concentration vs. time and calculate percent degradation of
CM398 in the reaction mixture. The elimination half-life
(T
1/2
) was calculated as Eq. 1.
T
1=2
¼ −0:693=k ð1Þ
Where k is the slope of the line obtained by plotting natural
logarithmic of percentage of CM398 remaining in the reaction
mixture vs. incubation time. Intrinsic clearance (CL
int
) and
whole liver clearance (CL
int,H
) were calculated from the
following equations:
CL
int
¼ k Incubation volumeðÞ= Microsomal proteinðÞð2Þ
CL
int;H
¼ CL
int
MPPGL liver scaling factor ð3Þ
where MPPGL represents the microsomal protein per gram of
Sprague Dawley rat liver (45 mg/g) (33), and liver scaling factor
(40 g/Kg) (34) represents the liver weight per body weight of
Sprague Dawley rats. In vivo hepatic clearance was extrapolated
through well-stirred model (Eq. 4) including microsomal protein
binding (f
umic
)(35). The f
umic
was derived using the equation
Table I. Binding affinities of CM398 for sigma and non-sigma receptors and specific conditions used for the competition binding assays
Target Ki
a
(nM) Tissue Radioligand Nonspecific binding
Sigma receptors Sigma-1
Sigma-2
560 ± 8.72
0.43 ± 0.015
Rat brain
Rat brain
5nM[
3
H](+)-pentazocine
3nM[
3
H]di-o-tolylguanidine
10 μM
haloperidol
10 μM
haloperidol
Monoamine transporters Dopamine 32.90 ± 1.9 Rat striatum 0.5 nM [
3
H]WIN 35,428 50 μM cocaine
Serotonin 244.2 ± 2.4 Rat brainstem 0.2 nM [
3
H]paroxetine 1.5 μM imipramine
Norepinephrine > 1000 Rat cerebral cortex 0.5 nM [
3
H]nisoxetine 4 μM desipramine
Other neurotransmitter receptors Dopamine (D
2
) > 1000 Rat brain 5 nM [
3
H](−)sulpiride 1 μM haloperidol
Serotonin (5-HT
2
) > 1000 Rat brain 2 nM [
3
H]ketanserin 1 μM mianserin
NMDA > 10,000 Rat brain 5 nM [
3
H]TCP 10 μM cyclazocine
Opioid >1000 Rat brain 1 nM [
3
H]naloxone 1 μM naloxone
a
Affinities (Ki values in nanomolar) were determined in brain tissue homogenates
The values represent ± S.E.M. from replicate assays. Values of > 10,000 represent less than 30% displacement of the radioligand at that
concentration.
94 Page 4 of 11 The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
(Eq. 5) of Hallifex and Houstan (36). Hepatic extraction ratio was
also determined using Eq. 6.
Hepatic Clearance CL
H
ðÞ
¼ Q f
u
CL
int
=f
umic
ðÞ= Q þ f
u
CL
int
=f
umic
ðÞðÞð4Þ
f
umic
¼ 1=1 þ C 10
0:072 logP=DðÞ
^
2þ0:067logP=D−1:126
ðÞ
ð5Þ
Hepatic extraction ratio ¼ CL
H
=Q ð6Þ
where f
u
(6.2%) is the unbound fraction of CM398 in rat
plasma, logP/D (3.1) is the partition coefficient, C is the
microsomal protein concentration, and Q is the hepatic blood
flow in Sprague Dawley rats (4.8 L/h/kg) (33).
Plasma Protein Binding Studies
The protein binding of CM398 was evaluated in vitro
using an ultra-filtration method at concentrations of 1 and
10 μM. The desired concentrations (1 and 10 μM) were
obtained by spiking the required volume of stock solutions in
rat plasma. Spiked organic content was ≤ 0.5% v/v. The
spiked plasma samples were placed in Centrifree® devices
(YM-30, Millipore, Bedford, USA) and incubated at 37°C for
30 min. The samples were then centrifuged for 10 min at
1000 g, and ultrafiltrates were collected. Spiked plasma and
plasma filtrate samples were processed and analyzed using
the UPLC-MS/MS method as described in supporting infor-
mation. Nonspecific binding was also determined and incor-
porated in the calculation of plasma protein binding values.
The fraction unbound (f
u
) and plasma protein binding were
calculated as described in Eqs. 7 and 8, respectively (37).
f
u
¼ C
f
= 1−NSBðÞ=C
i
½ ð7Þ
Protein binding ¼ 1− f
u
ðÞ100 ð8Þ
Where C
i
is the initial concentration, C
f
is the concentration
in filtrate or free compound, NSB is the nonspecific binding
fraction, and f
u
is the percent unbound drug concentration.
Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rats
Oral (20 mg/kg) and intravenous (1 mg/kg) pharmacoki-
netic (PK) studies of CM398 were evaluated in male Sprague
Dawley rats ( N 0 5, each). Right jugular vein cannulated rats
(225 ± 25 g) were purchased from Envigo (Indianapolis,
USA). Prior to the PK study, the animals were quarantined
in the University of Mississippi vivarium for 48 h with a 12-h
dark/light cycle and allowed access to standard feed and
water ad libitum. All animal experiments were performed in
accordance with the University of Mississippi Institutional
Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) pre-approved
protocol. Animals were housed in individual Nalgene
metabolic cages with mesh floor and receptacles for urine
and feces. Rodent feed was removed from the metabolic
cages 12–18 h prior to oral (P.O.) dosing, and feed was again
provided 4 h post-dose. Animals in the (I.V.) administration
study were allowed constant access to standard feed. All
animals always had access to water ad libitum. Solution
formulations of CM398 were prepared in water (5 mg/mL)
and normal saline (1 mg/mL) for P.O. and I.V. PK studies,
respectively. The formulation for the I.V. study was filtered
through 0.2 μmsyringefilter. Both formulations were
analyzed for CM398 content. The I.V. solutions were
administered via caudal vein. The P.O. solution was admin-
istered via oral gavage. Blood samples were collected using
the indwelling cannula. An initial blood volume of 0.05 mL
was withdrawn to clear the line of heparinized saline. Using a
fresh syringe, 0.15 mL of blood was withdrawn and placed in
heparin coated micro-centrifuge tube. The cannula was then
flushed with 0.20 ml of heparinized saline. For the P.O. study,
blood samples were taken pre-dose and at 0.17, 0.33, 0.5, 0.75,
1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h post-dose. For the I.V. study, blood
samples were taken pre- dose and at 0.083, 0.17, 0.33, 0.5, 1, 2,
4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h post-dose. Rat plasma was separated by
centrifugation of blood at 4000g for 10 min at 4°C and stored
at − 80°C refrigerator until analysis. Plasma samples were
processed and analyzed using an UPLC-MS/MS method as
described in supporting information. Plasma concentration-
time data and PK parameters are represented as mean ±
standard error of the mean (SEM). Peak plasma concentra-
tion (C
max
) and time to reach C
max
(T
max
) were obtained
directly from the concentration-time data plot. Concentration
vs. time data was subjected to noncompartmental analysis
using Phoenix WinNonlin (version 6.3; Certara Inc, Missouri,
USA). The area under plasma concentration-time curve
(AUC) of CM398 was calculated using the linear trapezoidal
method. Clearance (CL) was calculated as a ratio of dose and
AUC. Absolute oral bioavailability (%F) was calculated
using Eq. 9.
%F ¼ Dose
intravenous
AUC
lastðÞoral
=Dose
oralðÞ
AUC
lastðÞintravenous
100
ð9Þ
In Vivo Characterization in a Model of Inflammatory Pain
and Statistical Analysis
Thirty-five 10 weeks old male CD-1 mice obtained from
the Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, Massachusetts,
USA ,were used in the formalin assay. Mice were housed five
to a cage in a temperature and humidity-controlled room at
the University of Florida vivarium on a 12:12-h light/dark
cycle (lights off at 19:00 h) with free access to food and water
except during experimental sessions. All procedures were
pre-approved and carried out in accordance with the UF
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee as specified by
the 2011 National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and
Use of Laboratory Animals. Animal studies are reported in
compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines (38,39). Sample
sizes (i.e., number of animals) were predetermined by power
analysis, and animals were assigned to groups randomly. Drug
94 Page 5 of 11
The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
treatment experiments were conducted in a blinded fashion.
No animals were excluded from statistical analysis.
After seven mice each received a 10-min pre-treatment
with vehicle (saline, 0.9% as a control group), morphine
(23.2 μmol/kg, i.p. as a positive control), or CM398 (0.23,
2.32, or 23.2 μmol/kg, i.p.), formalin (10 μL of a 10%
solution) was injected into the hind paw as described
previously (40,41). Paw-licking duration (in s) during 5 min
intervals was recorded for 70 min. The summated response
during the final 60 min was analyzed, consistent with
nociception attributed to Phase II inflammation (41,42).
All paw-licking data for formalin testing are reported as
summed paw licking as area under the curve (AUC) by each
animal across the 60-min measured response, ± SEM. Mor-
phine data vs. saline was analyzed by Student ’s t test. CM398
data was analyzed by a one-way ANOVA (factor:dose) with
significant results between groups further analyzed with
Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. The data and
statistical analysis comply with the recommendations on
experimental design and analysis in pharmacology (43 ). All
data are presented as mean ± SEM, with a significance set at
P<0.05, denoted by the asterisk (*).
RESULT
Chemistry
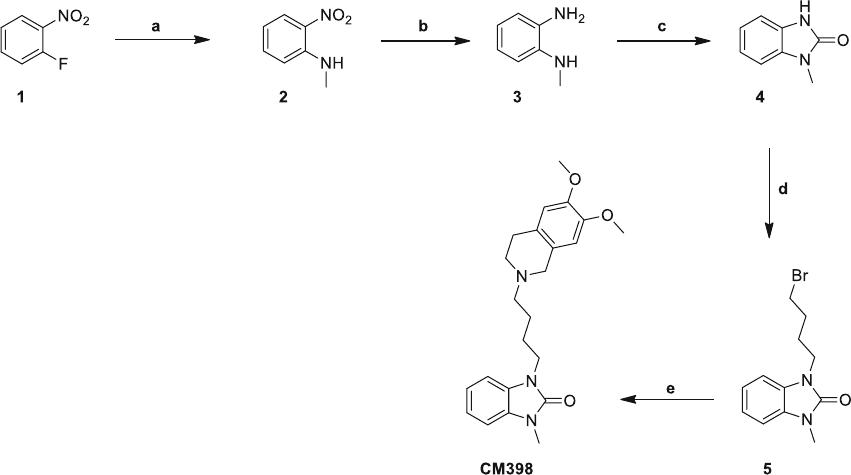
The straightforward synthetic scheme for CM398 is
outlined in Fig. 2. Treatment of 1-fluoro-2-nitro-benzene ( 1)
with 40% aqueous methylamine at room temperature gave
N-methyl-2-nitroaniline (2),whichwassubjectedtohydro-
genation (H
2
) in presence of 10% palladium on activated
charcoal to afford N
1
-methylbenzene-1,2-diamine (3)
(25,44,45). The later int ermediate was subje cted to ring
closure using 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) in anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran (THF) and heated to 65°C to obtain 1-
methyl-2-benzimidazolinone (4). Treatment of compound 4
with 1,4-dibromobutane in the presence of anhydrous
potassium carbonate in anhydrous dimethylformamide
(DMF) gave 5. The bromo derivative ( 5) was then coupled
with 6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline in the
presence of potassium carbonate in DMF to afford the
target compound (CM398). Spectral analysis and high-
resolution mass spectra of CM398 were consistent with its
assigned structure.
Competition Binding Assays
The binding affinity of CM398 for sigma-1 and sigma-2
receptor subtypes is summarized in Table I. CM398 possess
subnanomolar affinities for the sigma-2 receptor and over
1000-fold selectivity for the sigma-1 receptor. Moreover,
binding affinities versus other off-target proteins, including
monoamine transporter and other neurotransmitter recep-
tors, were also reported (Table I). The receptor binding
profile of CM398 is indicative of its highly preference for the
sigma-2 compared with the sigma-1 and to the other non-
sigma proteins (selectivity ratio > 1000). Furthermore, CM398
resulted highly selective also for the norepinephrine trans-
porter r eceptor (Ki > 1,000 nM) and for the serotonin
transporter receptor (500-fold); on the other hand, CM398
displayed significant affinity for the dopamine transporter (Ki
0 32.90 nM). However, because dopamine transmission is not
strictly related to nociception but rather it may reinforce the
noradrenergic effects to inhibit certain type of pain (46),
CM398 represented a suitable probe for the scope of this
study.
Fig. 2. Synthesis of CM398. Reagents and conditions: a CH
3
NH
2
,H
2
O, 2 h, r.t. b 10% Pd/C, H
2
(1 atm), MeOH, 2 h. c CDI,
THF, 65°C, 18 h. d 1,4-dibromobutane, K
2
CO
3
, DMF, 60°C, 2 h. e 6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, K
2
CO
3
,
DMF, 60°C, 1 h
94 Page 6 of 11 The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94

Metabolic Stability in Rat Liver Microsomes
It is important to understand the fate of a discovery
compound undergoing hepatic metabolism; therefore, meta-
bolic stability of CM398 was performed in rat liver micro-
somes. In vitro metabolic stability method i s able to
determine the metabolic depletion of a compound by
cytochrome P450 enzyme s in a closed system without
considering the physiological factors like blood flow or drug
binding within the matrix (35). The in vitro half-life of
CM398, when incubated in rat liver microsomes, was found
to be 0.10 ± 0 .01 h. The CL
int,H
derived from in vitro half-life
and scaling factors is 12.8 ± 0. 3 L/h/kg. Calc ulated value of
f
umic
was 0.63, which also suggests that only 37% of the
compound in liver will be available for metabolism by the
liver enzymes. In vitro CL
int,H
was also successfully extrap-
olated to hepatic clearance and extraction ratio. Compound
CM398 exhibited both high hepatic clearance (CL
H
,4.6±
0.0 L/h/Kg) and extraction ratio (0.96 ± 0.01). The high
extraction ratio suggests that only approximately 4% of
CM398 can escape unchanged after a single pass through
the liver following its phase I metabolism.
Plasma Protein Binding Studies
The reversible binding of a drug to plasma proteins is
an important determinant of its PK and pharmacodynamics
characteristics. The protein binding of CM398 was evalu-
ated in vitro using ultra-filtration method. The
concentration-dependent F
u
ofCM398wasstudiedinrat
plasma. At concentrations of 1 and 10 μM, the F
u
values
were 6.7 ± 1.1 and 5.6 ± 0.1%, respectively. Average plasma
protein binding of CM398 was found to be 93.8 ± 0.9%.
Non-specific binding of CM398 to Centrifree® devices was
less than 5.0%.
Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rats
The PK properties of CM398 were studied following the
P.O. (20 mg/kg) and I.V. (1 mg/kg) administration of the
compound to male Sprague Dawley rats. After dosing of
CM398, close and continuous visual monitoring of the
animals revealed that there was no severe acute toxicity
response, as non e of the animals showed any signs of
behavioral or neurological toxicity during the entire study
period. The plasma concentration-time profiles are presented
in Fig. 3. PK parameters were estimated using non-
compartmental analysis with Phoenix WinNonlin and are
presented in Table II. CM398 shows a very rapid absorption
as C
max
(2052.8 ± 252.8 ng/mL) occurred at 0.17 ± 0.00 h
(T
max
) post-dose. Oral a bsorption is so fast, that the
absorption phase cannot be captured. Absolute oral bioavail-
ability was calculated to be 29.0%, indicating adequate total
exposure after the oral dose. Total body CL (2.1 ± 0.1 L/h/kg)
of CM398 was lower than the total hepatic blood flow (4.8 L/
h/kg) (33) in rats, indicating negligible extra-hepatic elimina-
tion of the compound. The volume of distribution (V
d
, 5.3 ±
0.9 L/kg) of CM398 was larger than the total blood volume of
rats (0.085 L/kg) (34), showing extra-vascular distribution of
the compound. After P.O. and I.V. dosing, the mean half- life
(T
1/2
) was found to be 1.9 ± 0.2 and 1.7 ± 0.3 h, respectively.
In Vivo Characterization
The analgesic effects in vivo of CM398 were tested using
the formalin model of inflammatory pain in mice. Mice (n 0 7)
were pretreated wit h vehicle (saline, 0 .9%), m orphine
(23.2 μmol/kg), or CM398 (0.23, 2.32, or 23.2 μmol/kg )
through the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route and 10 min later,
administered formalin (10 μL in the hind paw). Mice
pretreated with saline spent an average of 205.1 ± 32.6 s
Fig. 3. Mean plasma concentration-time profile of CM398 in male Sprague Dawley rats
(N 0 5, each) after a single oral (20 mg/kg) and intravenous (1 mg/kg) administration. Bar
represents SEM
94 Page 7 of 11The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
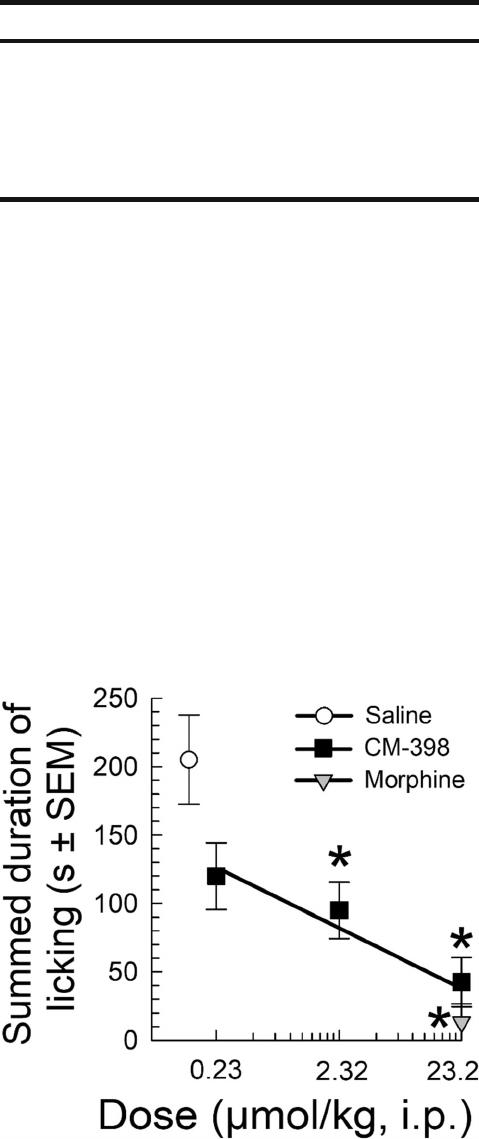
licking the injected hindpaw. Mice pretreated with morphine
spent significantly less time licking their formalin-treated
hindpaw (205.1 ± 32.6 s; p 0 0.0002, Student’s t test). Pretreat-
ment with CM398 dose dependently reduced the time spent
licking the hind paw (Fig. 4), demonstrating a significant
antinociceptive effect doses of 2.32 and 23.2 μmol/kg, i.p.
(F(3, 24) 0 7.66, p 0 0.0009; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s
post hoc test).
DISCUSSION
Previous research and preclinical studies have eluci-
dated the role of the sigma-1 receptor in modulating
nociception (8,47). In particular, the high expression of
sigma-1 receptors in specific areas of the brain such as
dorsal spinal cord, thalamus, periaqueductal gray,
basolateral amygdala, and rostroventral medulla (48), as
well as in peripheral tissues (especially dorsal root ganglia
neurons) (49), clearly suggests its involvement in pain
modulation.
From a pharmacological point of view, inhibition of
sigma-1 receptor produces a decrease of nociception stimuli
through attenuated expression of pain behaviors in several
animal models, including mechanical hypersensitivity (cap-
saicin-induced test), inflammatory pain (formalin assay),
and neuropathic pain models (SNI in mice) (50). Moreover,
these findings were s upported by previous studies which
used sigma-1 receptor KO mice (51–53).
In a more recent study, Sahn et al. have tested the effect
of IT injection of different sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptor
ligands in the mouse SNI model (24). As a result, both the
sigma-1 and the sigma-2/Tmem97 preferring ligands pro-
duced antinociceptive effects, which were significantly
different from vehicle, whereas the moderate selective
sigma-2 receptor agonist, siramesine, showed only a modest
inhibitory effect o n mechanical hypersensitivity (24). These
results led to further investigations into the putative role of
sigma-2 receptors in the modulation of pain. In fact, unlike
the results obtained for sigma-1 receptor antagonists, which
are consistent with previously reported literature, those
obtained by using slightly preferring sigma-2 receptor
ligands did not completely clarify if a mixed sigma-1/
sigma-2 or a selective sigma-2 compound might be benefi-
cial to treat pain. Unfortunately, as is often the case, the
lack of very selective ligands for the protein target adds
complexity for elucidating their function. From this per-
spective, the main goal of this work was the preliminary
characterization of a highly selective sigma-2 receptor
ligand w ith drug-like properties, serving as a lead candidate
for further preclinical and clinical development.
The radioligand binding assays revealed that CM398
displayed subnanomolar affinities (K i
0 0.43 nM) for the
sigma-2 receptor and very low affinities (Ki 0 560 nM) for
the sigma-1 receptor, thus, to the best of our knowledge,
CM398 represents the most selective sigma-2 receptor ligand
reported to date with regard to sigma-1/sigma-2 selectivity
ratio (1000-fold) (54). The binding properties of CM398 were
consistent with those of a recently reported set of structurally
related benzimidazolone-based analogs (25). Structure-
affinity relationships (SARs) studies suggested that the
presence of both the benzimidazolone as a scaffold and the
6,7-disubstituted tetrahydroisoquinolin e as a cyclic amine
fragment was optimal in term of sigma binding profile.
Specifically, replacement of the 1-(4-fluorophenyl)piperazine
(CM397, Fig.1) with the 6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinoline moiety significantly increased the
affinity for the sigma-2 receptor (Ki 0 2.5 and 0.43 nM) and
the selectivity over the sigma-1 receptor subtype (179-fold
and > 1000 fold, respectively).
CM398 also possessed negligible affinities for D
2
, 5-HT
2
,
NMDA, opioid receptors, and norepinephrine transporters
(1000–10,000 nM). CM398 did demonstrate notable affinity for
dopamine (Ki 0 32.90 nM) and serotonin transporters (Ki 0
244.2 nM), but these are still 76-fold and > 500-fold over the
Table II. Pharmacokinetic parameters of CM398 after oral dose and
intravenous administration in male Sprague Dawley rats
a
Parameters Oral Intravenous
C
max
(ng/mL)
T
max
(h)
AUC
0 → t
(ng h/L)
Vd (L/kg)
2052.8 ± 252.8
0.17 ± 0.00
2733.6 ± 293.4
6.2 ± 0.6
–
–
471.3 ± 23.6
5.3 ± 0.9
T1/2 (h) 1.9 ± 0.2 1.7 ± 0.3
CL (L/h/kg) 2.2 ± 0.2 2.1 ± 0.1
Bioavailability (%) 29.0 –
a
Each value represents the average of five rats dosed oral (20 mg/kg)
and intravenous (1 mg/kg); values are mean ± SEM.
AUC area under the plasma concentration-time curve, CL clearance,
C
max
plasma peak concentration, T
max
time to C
max
,T
1/2
elimination
half-life, V
d
volume of distribution
Fig. 4. Antinociceptive effects of CM398 in the formalin test. Values
represent summed time licking across 60 min testing period following
5% formalin injection into the mouse hindpaw. n 0 7 (each); *p 0 0.02
vs. vehicle response; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for
CM398 , or p 0 0.0002 vs. vehicle response; Student’s t test for
morphine
94 Page 8 of 11 The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
affinity for sigma-2 receptors. As mentioned above, the in vitro
pharmacologic profile of CM398 was well suited to unveil the
utility of sigma-2 ligands as potential therapeutic for pain
treatment, especially due to the lack of affinity with those
target proteins mainly involved in pain relief mechanisms, for
instance, opioid receptors, noradrenaline transporters, D
2
,and
NMDA receptors (55–59).
In regard to the pharmacokinetic evaluation, CM398
demonstrated adequate oral exposure, extravascular distribu-
tion, and negligible extra hepatic elimination in rats indicating
satisfactory pharmacokinetic properties to support its further
development as a pharmacological tool and potential orally
active drug candidate.
Finally, we decided to test the analgesic properties of
CM398 in a tonic pain stimuli induced by formalin injection
rather than allodynia elicited by chronic nerve injuries. The
formalin test is a standard animal model of inflammation-
induced nociception and frequently included in the battery of
behavioral pharmacology tests of pain (60).The2.32and23.2
μmol/kg i.p. doses of CM398 in mice produced a significant
reduction of the time spent licking as compared with saline,
through attenuation of the localized inflammatory pain
produced after injection of formalin in the paw of mice.
These results suggest that targeting sigma-2 r eceptor with a
highly selective ligand, like CM398, may be effective in
alleviating inflammatory pain. Notably, this initial testing was
limitedtomalemicetobeconsistentwiththeprevioustesting
(24). Although sex differences have not been demonstrated
in antinociception studies involving sigma-1 receptors
(51,52), future studies are needed to examine possible sex
effects on sigma-2 receptor-mediated a ntinociception. Al-
though the main goal of this work was limited to the
preliminary evaluation of the pharmacological profile of a
potent and highly selective sigma-2 receptor ligand, collec-
tively, this preliminary data offers support for further,
extensive characterization.
CONCLUSION
In summary, we synthesized and characterized CM398, a
highly selective sigma-2 receptor ligand, with the highest
sigma-1/sigma-2 selectivity ratio known to date. Moreover,
CM398 acted as a sigma-2 preferring ligand versus other non-
sigma receptors involved in pain modulation, p articularly
opioid receptors, NMDA, and norepinephrine transporters.
The metabolism studies perf ormed on CM398 showed
suitable drug-like properties for the development of an orally
active drug. Despite the favorable pharmacological profile of
CM398, additional evaluation of analgesic effects in a full
battery of behavioral models examining the various modal-
ities of pain is needed. The data provided herein represent
further support for the development of sigma-2 receptors
ligands as an alternative pain medication.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported, in part, by grants from the
National Institutes of Health NIDA R01 DA023205 (CRM,
RRM); NIMH P20 GM104932 (CRM, BAA); and from the
Department of Defense CMRMP PR161310/P1 (CRM, JPM).
REFERENCES
1. Colloca L, Ludman T, Bouhassira D, Baron R, Dickenson AH,
Yarnitsky D, et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2017;3:17002.
2. Yan YY, Li CY, Zhou L, Ao LY, Fang WR, Li YM. Research
progress of mechanisms and drug therapy for neuropathic pain.
Life Sci. 2017;190:68–77.
3. NIH NIoNDaS-. Peripheral Neuropathy Fact Sheet 2018
[July 06, 2018]. Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Dis-
orders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/ Fact-Sheets/Pe ripheral-
Neuropathy-Fact-Sheet.
4. Cruccu G, Truini A. A review of neuropathic pain: from
guidelines to clinical practice. Pain Ther. 2017;6(Suppl 1):35–42.
5. Calandre EP, Rico-Villademoro s F, Slim M. Alpha(2)delt a
ligands, gabapentin, pregabalin and mirogabalin: a review of
their clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use. Expert Rev
Neurother. 2016;16(11):1263–77.
6. Yaksh TL, Wallace MS. Opioids, analgesia, and pain manage-
ment. In: Goodman and Gilman’s the Pharmacological Basis of
Therapeutics. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2011. p. 481–
526.
7. Bouhassira D, Attal N. Emerging therapies for neuropathic
pain: new molecules or new indications for old treatments?
Pain. 2018;159(3):576–82.
8. Merlos M, Burgueno J, Portillo-Salido E, Plata-Salaman CR,
Vela JM. Pharmacological modulation of the sigma 1 receptor
and the treatment of pain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:85–107.
9. Kim FJ. Introduction to sigma proteins: evolution of the concept
of sigma receptors. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;244:1–11.
10. Hanner M, Moebius FF, Flandorfer A, Knaus HG, Striessnig J,
Kempner E, et al. Purification, molecular cloning, and expres-
sion of the mammalian sigma1-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci
U S A. 1996;93(15):8072–7.
11. Schmidt HR, Zheng S, Gurpinar E, Koehl A, Manglik A, Kruse
AC. Crystal structure of the human sigma1 receptor. Nature.
2016;532(7600):527–30.
12. Alon A, Schmidt HR, Wood MD, Sahn JJ, Martin SF, Kruse
AC. Identification of the gene that codes for the sigma2
receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(27):7160–5.
13. Diaz JL, Cuberes R, Berrocal J, Contijoch M, Christmann U,
Fernandez A, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the 1-
arylpyrazole class of sigma(1) receptor antagonists: identifica-
tion of 4-{2-[5-methyl-1-(napht halen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-3-
yloxy]ethyl}morpholine (S1RA, E-52862). J Med Chem.
2012;55(19):8211–24.
14. Lan Y, Chen Y, Cao X, Zhang J, Wang J, Xu X, et al. Synthesis
and biological evaluation of novel sigma-1 receptor antagonists
based on pyrimidine scaffold as agents for treating neuropathic
pain. J Med Chem. 2014;57(24):10404–23.
15. Romeo G, Prezzavento O, Intagliata S, Pittalà V, Modica MN,
Marrazzo A, et al. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo characteriza-
tion of new benzoxazole and benzothiazole-based sigma recep-
tor ligands. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;174:226–35.
16. Cirino TJ, Eans SO, Medina JM, Wilson LL, Mottinelli M,
Intagliata S, et al. Characterization of sigma 1 receptor
antagonist CM-304 and its analog, AZ-66: novel therapeutics
against Allodynia and induced pain. Front Pharmacol.
2019;10:678.
17. Vidal-Torres A, de la Puente B, Rocasalbas M, Tourino C, Bura
SA, Fernandez-Pastor B, et al. Sigma-1 receptor antagonism as
opioid adjuvant strategy: enhancement of opioid antinociception
without increasing adverse effects. Eur J Pharmacol.
2013;711(1–3):63–72.
18. Abadias M, Escriche M, Vaque A, Sust M, Encina G. Safety,
tolerability and pharmacokinetics of single and multiple doses of
a novel sigma-1 receptor antagonist in three randomized phase I
studies. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;75(1):103–17.
19. James ML, Shen B, Zavaleta CL, Nielsen CH, Mesangeau C,
Vuppala PK, et al. New positron emission tomography (PET)
radioligand for imaging sigma-1 receptors in living subjects. J
Med Chem. 2012;55(19):8272–82.
94 Page 9 of 11The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
20. Shen B, Park JH, Hjornevik T, Cipriano PW, Yoon D, Gulaka
PK, et al. Radiosynthesis and first-in-human PET/MRI evalua-
tion with clinical-grade [(18)F]FTC-146. Molecular imaging and
biology : MIB : the official publication of the academy of. Mol
Imaging. 2017;19(5):779–86.
21. Shen B, Behera D, James ML, Reyes ST, Andrews L, Cipriano
PW, et al. Visualizing nerve injury in a neuropathic pain model
with [(18)F]FTC-146 PET/MRI. Theranostics. 2017;7(11):2794–
805.
22. Hjornevik T, Cipriano PW, Shen B, Park JH, Gulaka P, Holley
D, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of (18)F-FTC-
146 i n huma ns. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med.
2017;58(12):2004–9.
23. Zamanillo D, Romero L, Merlos M, Vela JM. Sigma 1 receptor:
a new therapeutic target for pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;716(1–
3):78–93.
24. Sahn JJ, Mejia GL, Ray PR, Martin SF, Price TJ. Sigma 2
receptor/Tmem97 agonists produce long lasting antineuropathic
pain effects in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017;8(8):1801–11.
25. Intagliata S, Alsharif WF, Mesangeau C, Fazio N, Seminerio
MJ, Xu YT, et al. Benzimidazolone-based selective σ2 receptor
ligands: synthesis and pharmacological evaluation. Eur J Med
Chem. 2019;165:250–7.
26. Mesangeau C, Narayanan S, Green AM, Shaikh J, Kaushal N,
Viard E, et al. Conversion of a highly selective sigma-1 receptor-
ligand to sigma-2 receptor preferring ligands with anticocaine
activity. J Med Chem. 2008;51(5):1482–6.
27. Nicholson HE, Alsharif WF, Comeau AB, Mesange au C,
Intagliata S, Mottinelli M, et al. Divergent cytotoxic and
metabolically stimulativ e functions of sigma-2 receptors:
structure- activity relationships of 6-acetyl-3-(4-(4-(4-
fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)benzo[d]oxazol- 2(3H)-one
(SN79) derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018;7.
28. Robson MJ, Turner RC, Naser ZJ, McCurdy CR, O'Callaghan
JP, Huber JD, et al. SN79, a sigma recept or antagonist,
attenuates methamphetamine-induced astrogliosis through a
blockade of OSMR/gp130 signaling and STAT3 phosphoryla-
tion. Exp Neurol. 2014;254:180–9.
29. Katz JL, Hiranita T, Kopajtic TA, Rice KC, Mesangeau C,
Narayanan S, et al. Blockade of cocaine or sigma receptor
agonist self administration by subtype-selective sigma receptor
antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016;358(1):109–24.
30. Obeng S, Patel A, Burns M, Intagliata S, Mottinelli M, Reeves
ME, et al. The sigma1 receptor antagonist CM304 potentiates
the antinociceptive but not the discriminative stimulus effects of
the cannabinoid receptor agonist THC in rats. FASEB J.
2020;34(S1):1.
31. Patel A, Obeng S, Burns M, Intagliata S, Mottinelli M, Reeves
ME, et al. The sigma1 receptor antagonist CM304 enhances the
antinociceptive effects of the cannabinoid receptor agonists, but
not Mu-o pioid receptor full agonists in mice. FASEB J.
2020;34(S1):1.
32. Matsumoto RR, McCracken KA, Pouw B, Zhang Y, Bowen
WD. Involvement of sigma receptors in the behavioral effects of
cocaine: evidence from novel ligands andantisense
oligodeoxynucleotides. Neuropha rmacology. 2002;42(8):1043–
55.
33. Peters SA. Physiol ogical ly-based phar macokinetic (PBPK)
modeling and simulations: principles, methods, and applications
in the pharmaceutical industry: John Wiley & Sons; 2012.
34. Davies B, Morris T. Physiological parameters in laboratory
animals and humans. Pharm Res. 1993;10(7):1093–5.
35. Khojasteh SC, Wong H, Hop CE. Drug metabolism and
pharmacokinetics quick guide: Springer Science & Business
Media; 2011.
36. Hallifax D, Houston JB. Binding of drugs to hepatic micro-
somes: comment and assessment of current prediction
methodology with recommendation for improvement. Drug
Metab Dispos. 2006;34(4):724–6.
37. Lee K-J, Mower R, Hollenbeck T, Castelo J, Johnson N,
Gordon P, et al. Modulation of nonspecific binding in ultrafil-
tration protein binding studies. Pharm Res. 2003;20(7):1015–21.
38. Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG.
Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines
for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(6):e1000412.
39. McGrath JC, Lilley E. Implementing guidelines on reporting
research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): new requirements for
publication in BJP. Br J Pharmacol. 2015;172(13):3189–93.
40. Wheeler-Aceto H, Porreca F, Cowan A. The rat paw formalin
test: comparison of noxious agents. Pain. 1990;40(2):229–38.
41. Gong N, Huang Q, Chen Y, Xu M, Ma S, Wang Y-X. Pain
assessment using the rat and mouse formalin tests. Bio-protocol.
2014;4(21):e1288.
42. Cheng HY, Pitcher GM, Laviolette SR, Whishaw IQ, Tong KI,
Kockeritz LK, et al. DREAM is a critical transcriptiona l
repressor for pain modulation. Cell. 2002;108(1):31–43.
43. Curtis MJ, Bond RA, Spina D, Ahluwalia A, Alexander SP,
Giembycz MA, et al. Experimental design and analysis and their
reporting: new guidance for publication in BJP. Br J Pharmacol.
2015;172(14):3461–71.
44. Intagliata S, Modica MN, Pittala V, Salerno L, Siracusa MA,
Cagnotto A, et al. New N- and O-arylpiperazinylalkyl pyrimi-
dines and 2-methylquinazolines derivatives as 5-HT7 and 5-
HT1A receptor ligands: synthesis, structure-activity relation-
ships, and molecular modeling studies. Bioorg Med Chem.
2017;25(3):1250–9.
45. Modica MN, Intagliata S, Pittala V, Salerno L, Siracusa MA,
Cagnotto A, et al. Synthesis and binding properties of new long-
chain 4-substituted piperazine derivatives as 5-HT(1)a and 5-
HT(7) receptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
2015;25(7):1427–30.
46. Obata H. Analgesic mechanisms of antidepressants for neuro-
pathic pain. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11).
47. Merlos M, Romero L, Zamanillo D, Plata-Salaman C, Vela JM.
Sigma-1 receptor and pain. Handb Exp Pharmacol.
2017;244:131–61.
48. Alonso G, Phan V, Guillemain I, Saunier M, Legrand A, Anoal
M, et al. Immunocytochemical localizatio n of the sigma(1)
receptor in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience.
2000;97(1):155–70.
49. Bangaru ML, Weihrauch D, Tang QB, Zoga V, Hogan Q, Wu
HE. Sigma-1 receptor expression in sensory neurons and the
effect of painful peripheral nerve injury. Mol Pain. 2013;9:47.
50. Romero L, Zamanillo D, Nadal X, Sanchez-Arroyos R, Rivera-
Arconada I, Dordal A, et al. Pharmacological properties of
S1RA, a new sigma-1 receptor antagonist that inhibits neuro-
pathic pain and activity-induced spinal sensitization. Br J
Pharmacol. 2012;166(8):2289–306.
51. Entrena JM, Cobos EJ, Nieto FR, Cendan CM, Gris G, Del
Pozo E, et al. Sigma-1 receptors are essential for capsaicin-
induced mechanical hypersensitivity: studies with selective
sigma-1 ligands and sigma-1 knockout mice. Pain.
2009;143(3):252–61.
52. Cendan CM, Pujalte JM, Portillo-Salido E, Montoliu L,
Baeyens JM. Formalin-induced pain is reduced in sigma(1)
receptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;511(1):73–4.
53. de la Puente B, Nadal X, Portillo-Salido E, Sanchez-Arroyos R,
Ovalle S, Palacios G, et al. Sigma-1 receptors regulate activity-
induced spinal sensitization and neuropathic pain after periph-
eral nerve injury. Pain. 2009;145(3):294–303.
54. Nastasi G, Miceli C, Pittalà V, Modica MN, Prezzavento O,
Romeo G, et al. S2RSLDB: a comprehensive manually curated,
internet-accessible database of the sigma-2 receptor selective
ligands. J Cheminformatics. 2017;9:3.
94 Page 10 of 11 The AAPS Journal (2020) 22:94
