
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Sodium copper chlorophyllin attenuates adenine-induced chronic
kidney disease via suppression of TGF-beta and inflammatory
cytokines
Sachin V. Suryavanshi
1
& Milind Gharpure
2
& Yogesh A. Kulkarni
1
Received: 20 January 2020 /Accepted: 17 May 2020
#
Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Abstract
The present study was designed to evaluate the effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin (SCC) in adenine-induced chronic kidney
disease (CKD). CKD was induced in male Wistar rats by feeding 0.3% w/w adenine diet for 28 days. After induction, animals
were treated with sodium copper chlorophyllin at dose 2.7, 5.4, and 10.8 mg/kg for the next 28 days. The biochemical and urines
parameters like creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), albumin, total protein creatinine clearance, urea clearance, and glomerular
filtration rate were assessed on days 0, 14, and 28. Plasma TGF-β1, COX-2, and IL-6 levels were assessed. Various oxidative
stress parameters and TGF-β1 expression were determined in the kidney. Histopathology of the kidney was studied with different
stains. Sodium copper chlorophyllin-treated animals showed a significant reduction in urine output and relative kidney weight.
The treatment with sodium copper chlorophyllin significantly improved kidney function by normalizing biochemical and urine
parameters. Treatment with SCC significantly reduced circulatory inflammatory mediato rs—TGF-β1, COX-2, and IL-6.
Additionally, the treatment also significantly reduced oxidative stress and TGF-β1 expression in kidney tissues.
Histopathology studies showed inhibition in the kidney damage due to the treatment of SCC. The sodium copper chlorophyllin
treatment attenuated adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats.
Keywords Adenine
.
Chronic kidney disease
.
Sodium co pper chloroph yl lin
.
Chlorophyll derivative
.
Oxidative stress
.
Inflammation
Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major health problem and
the leading cause of mortality affecting the quality of life
worldwide (Perico and Remuzzi 2016). The CKD is linked
with acute kidney injury, cardiovascular dysfunction, and end-
stage renal disorder (ESRD) (Perico and Remuzzi 2016). The
global prevalence of CKD is between 11 and 16% (Hill et al.
2016). The limited treatment approaches for CKD necessitate
researchers to search for novel therapeutic agents especially
from natural sources. CKD is characterized by a mild or mod-
erate decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), increased
albuminuria, proteinuria and hematuria, and finally renal fail-
ure. Reactive oxygen species and inflammation play a key role
in kidney injury (Scholze et a l. 2016; Suryavanshi a nd
Kulkarni 2017). Elevated oxidative stress in the kidney is
responsible for activation of inflammatory cascade and acti-
vation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines like
TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2, and TGF-β (Suryavanshi and
Kulkarni 2017). Activation of these markers initiates the in-
flammatory and apoptotic process in the kidney, thereby kid-
ney damage (Garud and Kulkarni 2014, 2017a).
Sodium copper chlorophyllin, a USFDA-approved color, is
a chlorophyll derivative and it has been proved for its antiox-
idant, anti-aging, and antibacterial activity. It has also shown
significant effects in cancer management (Vasily 2015;
McCook et al. 2016;Vaňková et al. 2018). Additionally, so-
dium copper chlorophyllin has TGF-β and COX-2 inhibitory
activity (Thiyagarajan et al. 2014).
Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article
(https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01912-3) contains supplementary
material, which is available to authorized users.
* Yogesh A. Kulkarni
yogesh.kulkarni@nmims.edu; yogeshkulkarni101@yahoo.com
1
Shobhaben Pratapbhai Patel School of Pharmacy & Technology
Management, SVKM’s NMIMS, V. L. Mehta Road, Vile Parle (W),
Mumbai 400056, India
2
Thinq Pharma-CRO Ltd., A-30, Road No. 10, MIDC, Wagle Estate,
Thane 400604, India
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01912-3

Adenine diet-induced CKD is a more stable model and sim-
ilar to CKD in humans (Diwan et al. 2018). Adenine diet pro-
duces similar pathological conditions as that of CKD in humans
like tubulointerstitial fibrosis, vessel calcification, tubular atro-
phy, and crystal formation in the kidney (Diwan et al. 2018).
Adenine also elevates blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels
(Claramunt et al. 2015). Hence, the present study was designed
to evaluate the effect of sodium coppe r chlorophyllin in
adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats.
Materials and methods
Chemicals
Sodium copper chlorophyllin was procured from Shandong
Hanxing Biotech Co. Ltd., China. Adenine was procured from
Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). ELISA kits of TGF-β1
and COX-2 were procured from KinesisDx (California, USA)
and IL-6 E LISA kit w as procured Krishgen B iosystems
(India). Primary antibodies like TGF-β1, β-actin, and second-
ary antibody m-IgGk BP-HRP were procured from Santa
Cruz Biotechnology (Texas, USA).
Experimental animals
Necessary regulatory approval was taken from Institutional
Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) prior to starting experimen-
tal work. Male Wistar rats weighing between 160 and 180 g
were procured from the National Institute of Biosciences,
Pune, India. The animals were housed in the animal facility
under standard laboratory conditions and allowed to acclima-
tize for 1-week prior experimentation.
The animals were randomized into five different groups con-
taining 10 animals each according to their body weight. One
group was kept as the normal control group which received a
normal diet. Chronic kidney disease was induced in four groups
using adenine in the diet which is a well-accepted animal model
for CKD (Ali et al. 2013; Diwan et al. 2017; Törmänen et al.
2017). The animals received 0.3% w/w adenine in a powdered
diet for 28 days. After 28 days, one group was kept as disease
control which received no treatment while three groups were
treated with sodium copper chlorophyllin at dose 2.7, 5.4, and
10.8 mg/kg, orally. Sodium copper chlorophyllin was dissolved
in distilled water and administered by using oral gavage. The
treatment was given for 28 days.
Evaluation parameters
Body weight, food, and water intake
Body weight, food, and water intake of all animals were mea-
sured on the 14
th
and 28
th
day after specific treatment.
Biochemical parameters
Various biochemical parameters like plasma creatinine, pro-
tein, albumin, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were assessed
on the 14
th
and 28
th
day using commercially available kits
(Transasia Biomedicals Ltd., India).
Urine parameters
Urine was collected every fortnight using metabolic cages
(BIK Industries, India). Animals were kept individually in
metabolic cages and urine was collected for 24 h. Urine pa-
rameters like urine volume, protein, albumin, creatinine clear-
ance, urea clearance, and glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
were assessed. The creatinine clearance, urea clearance, and
GFR were calculated as per the previously described method
(Pestel et al. 2007) using the following formulae.
Creatinine clearance ml=minðÞ
¼
urine creatinine mg=dlðÞurine volume ml=minðÞ
plasma creatinine mg=dlðÞ
Urea clearance ml=minðÞ
¼
urine urea mg=dlðÞurine volume ml=minðÞ
plasma urea mg=dlðÞ
GFR ml=minðÞ
¼
creatinine clearance ml=minðÞþurea clearance ml=minðÞ
2
ELISA assays
Estimation of inflammatory markers like TGF-β1, COX-2,
and IL-6 levels was carried out in plasma using ELISA assay
kits.
Kidney hypertrophy and gross necropsy
At the end of the study, animals were sacrificed and the kid-
neys were isolated. The relative kidney weight was deter-
mined by dividing kidney weight with a body weight of the
animal. The gross necropsy of the kidneys was carried out.
Oxidative stress parameters
The oxidative stress in the kidney tissue was assessed by mea-
suring malondialdehyde (MDA) (Ohkawa et al. 1979;Garud
and Kulkarni 2017b), reduced glutathione (GSH) (Ellman
1959), catalase (Luck 1965), and superoxide dismutase
(SOD) levels (Paoletti et al. 1990).
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
0
14
28
150
200
250
300
350
400
*
**
**
**
***
***
Treatment Days
)g(thgieWy
d
oB
0
14
28
20
30
40
50
60
Treatment Days
Food Intake (g/day)
0
14
28
20
30
40
50
60
***
***
***
**
***
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
Treatment Days
)
ya
d/l
m(
ek
at
nI
r
eta
W
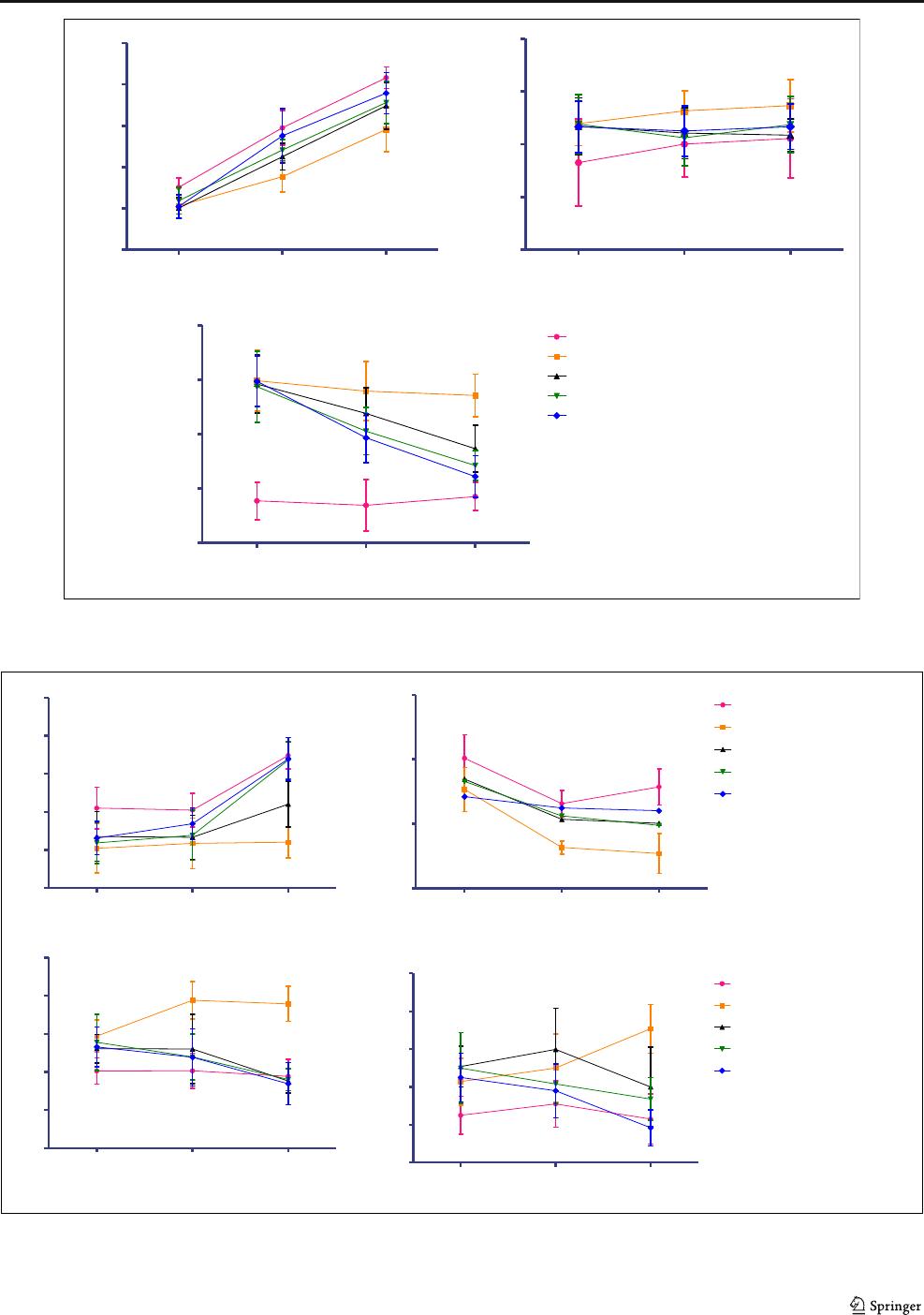
Fig. 1 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin (SCC) on body weight, food intake, water intake. All data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 10). The data
were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni’s test. *p <0.05,**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared with disease control
0
14
28
5
6
7
8
9
10
***
***
***
Treatment Days
)ld/g(nietorPlatoTams
a
lP
0
14
28
3
4
5
6
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
***
***
***
***
Treatment Days
Plasma Albumin (g/dl)
0
14
28
0
10
20
30
40
50
***
***
Treatment Days
)ld/gm(ne
g
ortiNaerUd
o
olB
0
14
28
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
***
***
***
Treatment Days
Plasma Creatinine (mg/dl)
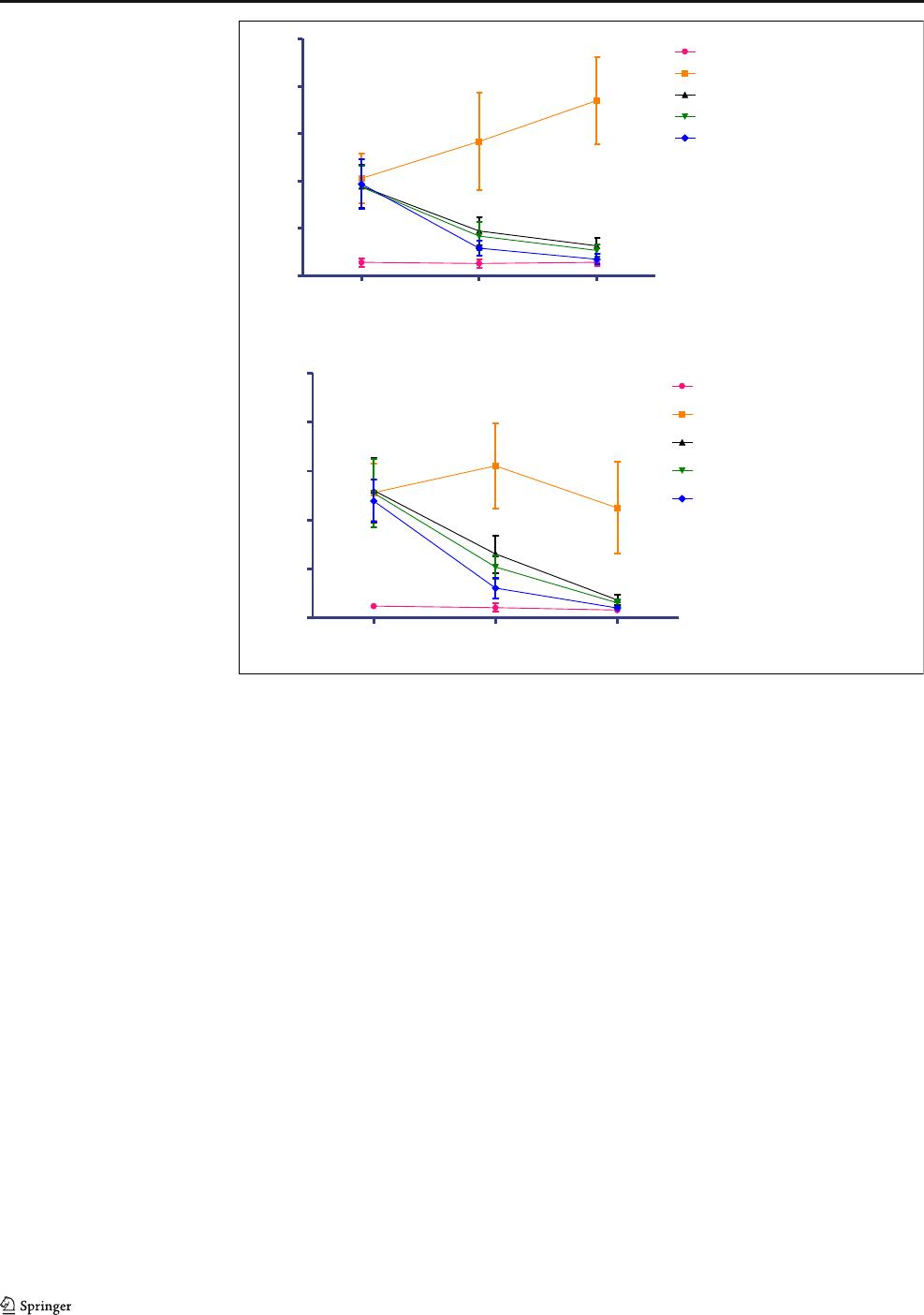
Fig. 2 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin (SCC) on biochemical parameters. All data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 10). The data was analyzed
using two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni’stest.*p <0.05,**p <0.01,***p < 0.001 when compared with disease control
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
Western blotting
Kidney tissues were minced with radioimmunoprecipitation
assay (RIPA) buffer to extract proteins. The protein content
was determined by the Lowry method (Lowry et al. 1951).
One hundred micrograms of protein was loaded and s epa-
rated on 10% acrylamide gel on Mini Trans-Blot® electro-
phoretic transfer cell (Bio-Rad, USA). Protein transfer was
carried out on the PVDF membrane (0.45 μm, Merck
Milipore, Germany) using a tris-glycine transfer buffer
containing 20% methanol at constant volt (100 V) for 1
h. Blocking was carried ou t with freshly pre pared 5%
non-fat dried milk powder in Tris buffer saline (TBS) so-
lution for 2 h. Primary antibody treatment of TGF-β1and
β-actin was given at dilution 1:1000 and 1:2000 respec-
tively for 2 h. Three washings of 15 min each were per-
formed with TBS c ontaining 0.1% tween 20. Secondary
antibody treatment (m-IgGk B P-HRP) was given at dilu-
tion 1:10,000 for 1 h. After washings, the bands were vi-
sualized with Clarity western ECL substrate (Bio-Rad,
USA) on X-ray films. The expressions were analyzed with
software Image Studio Lite version 5.2 (LI-COR
Biosciences, USA).
Histopathology study
The histopathological changes in kidney tissues were assessed
with Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) stain, Periodic acid–Schiff
(PAS) and trichrome staining as described previously (Garud
and Kulkarni 2017a). Fixed kidney tissues were embedded in
paraffin wax and thin sections of size 5 μmweretakenwitha
microtome (Leica, Germany). Slides were stained with differ-
ent stains. The prepared slides were examined under a micro-
scope to note histopathological lesions. The severity of lesions
was recorded as 0, no abnormality detected; 1, minimal (<
1%); 2, mild (1–25%); 3, moderate (26–50%); 4, moderately
severe/marked (51–75%); and 5, severe (76–100%), and dis-
tribution was recorded as focal, multifocal, and diffuse. The
glycogen content and collagen deposition were determined by
measuring the optical density of PAS-stained and trichrome-
stained microphotographs. The optical density was measured
using ImageJ software (NIH, USA).
Statistical analysis
All the data was expressed as mean ± SD. Data on the body
weight, food intake, water intake, ur ine parameters,
0
14
28
0
50
100
150
200
250
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
***
***
Treatment Days
)yad/gm(
n
oitercxe
n
imub
lA
0
14
28
0
200
400
600
800
1000
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
***
***
Treatment Days
)yad/gm(noitercxenietorP
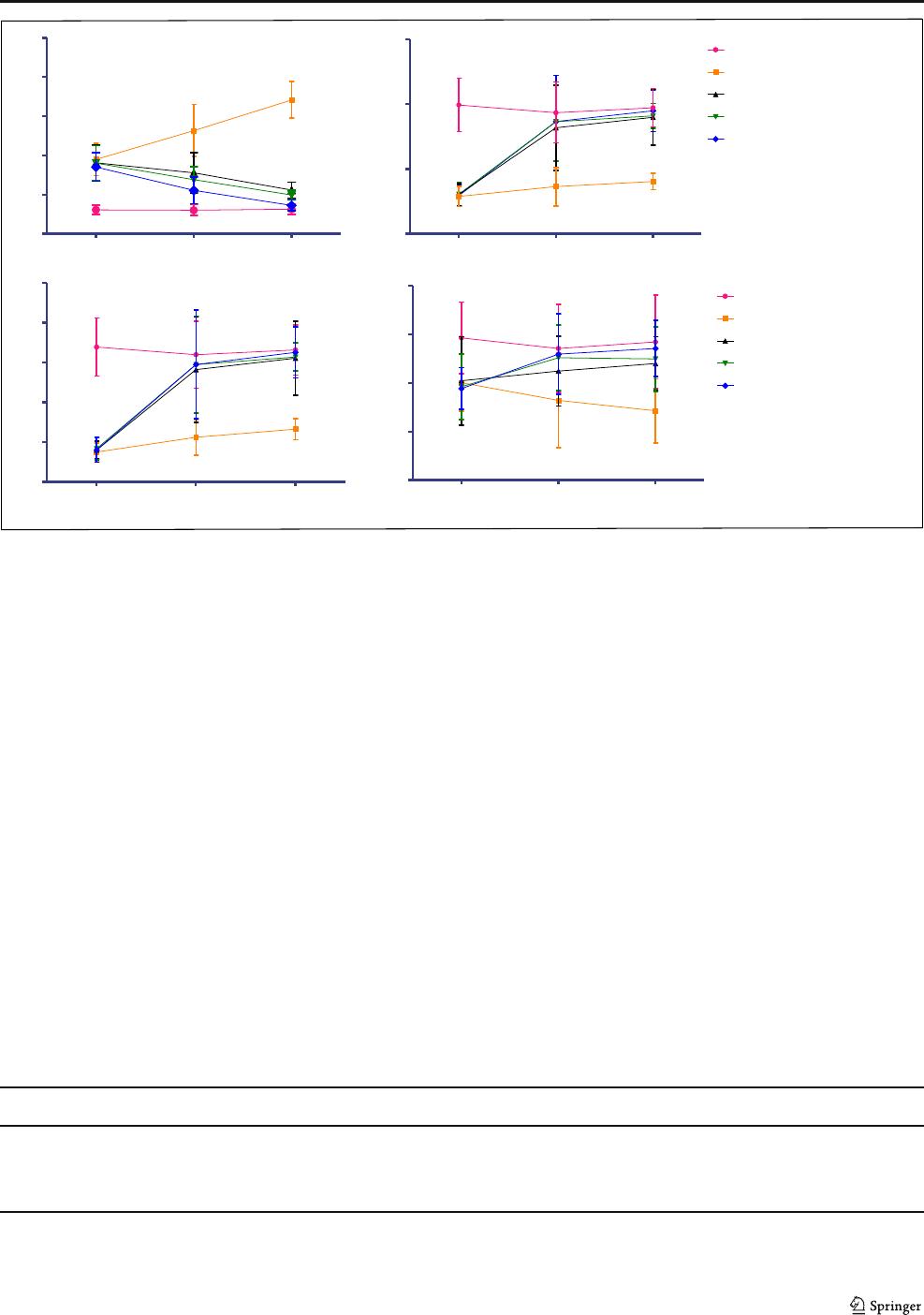
Fig. 3 Effect of sodium copper
chlorophyllin (SCC) on urine al-
bumin and protein. All data are
expressed as mean ± SD (n =10).
The data was analyzed using two-
way ANOVA followed by post
hoc Bonferroni’s test. ***p <
0.001 when compared with dis-
ease control
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
biochemical parameters, urea clearance, creatinine clearance,
and glomerular filtration rate was analyzed using two-way
ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc tests. Relative
kidney weight, oxidative stress parameters, and ELISA assays
were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by
Dunnett’s multiple comparisons.
Results
Body weight, food, and water intake
The body weight was significantly reduced in adenine-treated
animals. Sodium copper chlorophyllin treatment showed a
significant increase in body weight when compared with the
adenine-treated group (Fig. 1). The adenine-treated group
showed a significant increase in food and water consumption
as compared with animals in the normal group. Treatment
with sodium copper chlorophyllin did not alter the food con-
sumption but it significantly reduced the water consumption
compared with adenine-treated animals (Fig. 1).
Biochemical parameters
The creatinine and BUN levels were significantly increased (p
< 0.001) in disease control animals indicating significant kid-
ney damage. On the 28
th
day of treatment with sodium copper
chlorophyllin, all selected dose levels showed a significant
reduction (p < 0.001) in plasma creatinine levels when com-
pared with the disease control (Fig. 2). Similarly, the blood
urea nitrogen was also significantly reduced in sodium copper
chlorophyllin-treated animals at dose 2.7, 5.4, and 10.8 mg/kg
(p < 0.001) when compared with the disease control (Fig. 2).
Plasma albumin and protein levels were significantly de-
creased in disease control when compared with normal ani-
mals. Sodium copper chlorophyllin-treated animals
0
14
28
0
10
20
30
40
50
***
***
Treatment Days
)
y
ad/
l
m(
e
mu
lo
ven
i
rU
0
14
28
0
1
2
3
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
***
***
Treatment Days
GFR (ml/min)
0
14
28
0
1
2
3
4
5
***
***
Treatment Days
)ni
m
/
l
m(
ec
na
r
aelCaerU
0
14
28
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
***
**
*
*
Treatment Days
Creatinine clearance (ml/min)
Fig. 4 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin (SCC) on urine output, urea clearance, creatinine clearance, and GFR. All data are expressed as mean ± SD
(n = 10). The data was analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni’s test. ***p < 0.001 when compared with disease control
Table 1 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin on TGF-β1, COX-2, and IL-6 levels in plasma
Parameter Normal control Disease control Cu-chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg) Cu-chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg) Cu-chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
TGF-β1 (ng/ml) 36.16 ± 5.59 49.06 ± 8.48### 41.69 ± 5.09* 40.46 ± 3.68** 38.29 ± 5.17***
COX-2 (ng/ml) 8.114 ± 0.70 14.38 ± 2.60### 11.24 ± 3.35* 9.419 ± 1.78*** 8.763 ± 1.82***
IL-6 (pg/ml) 314.00 ± 46.97 404.80 ± 49.98### 323.30 ± 53.00** 318.70 ± 42.73** 318.50 ± 52.76**
All data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 10). The data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’stest.*p <0.05,**p <0.01,
***p < 0.001 when compared with disease control. ###p < 0.001 when compared with normal control
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
significantly increased (p < 0.001) plasma albumin and total
protein levels at all selected doses (Fig. 2).
Urine parameters
Urine protein and albumin levels were significantly increased
(p < 0.001) in adenine-treated animals when compared with
normal animals. Sodium copper chlorophyllin treatment sig-
nificantly reduced (p < 0.001) urine protein and albumin at all
selected dose levels as compared with adenine-treated animals
(Fig. 3).
The urine output was significantly increased in adenine-
treated animals (p <0.001)whencomparedwithnormalani-
mals. Treatment with sodium copper chlorophyllin signifi-
cantly reduced (p < 0.001) urine output at all selected dose
levels as compared with disease control. The creatinine clear-
ance, urea clearance, and GFR were significantly decreased (p
< 0.001) in adenine-treated animals when compared with the
normal group. Sodium copper chlorophyllin treatment signif-
icantly improved (p < 0.001) renal function at all selected dose
levels by improving renal creatinine, urea clearance, and GFR
when compared with adenine-treated animals (Fig. 4).
Estimation of inflammatory markers
The COX-2, IL-6, and TGF-β1 levels were significantly ele-
vated in the adenine-tre ated animals when compared with
normal animals. The sodium copper chlorophyllin treatment
significantly reduced the COX-2, IL-6, and TGF-β1levelsat
all selected dose levels on day 28 (Table 1).
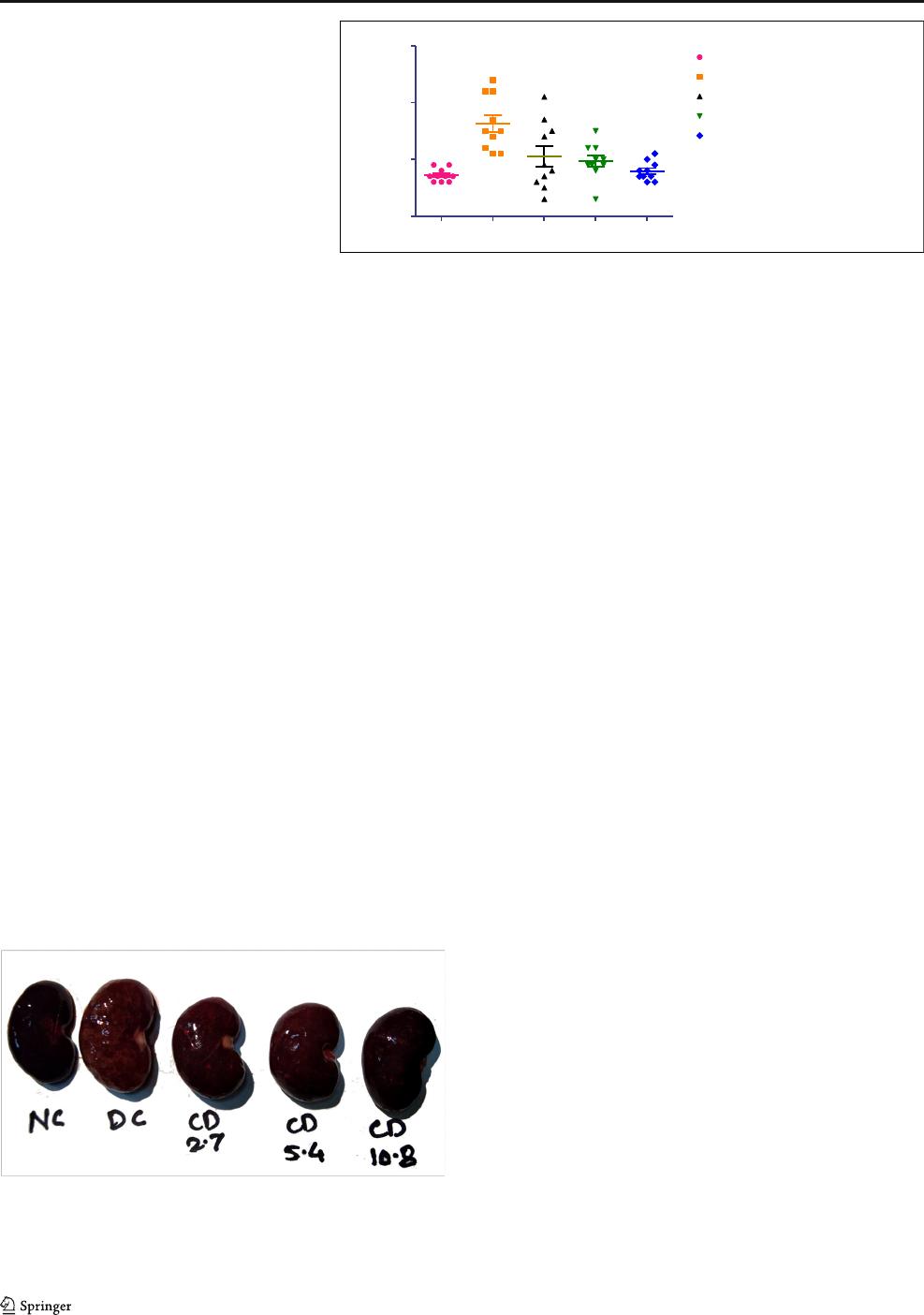
Kidney hypertrophy and gross necropsy
The relative kidney weight is an indicator of kidney hypertro-
phy. Animals in the adenine diet group showed significantly
high relative kidney weight when compared with normal an-
imals. Treatment of sodium copper chlorophyllin significantly
reduced relative kidney weight and thus hypertrophic condi-
tion at a dose of 2.7 mg/kg (p < 0.01), 5.4 mg/kg (p <0.01),
and 10.8 mg/kg (p < 0.001) when compared with the disease
control (Fig. 5). In gross necropsy, the kidneys of the adenine-
treated group showed abnormal structural changes and in-
creased average kidney weight as compared with normal an-
imals. The kidneys of normal control group anim als were
reddish-brown in color while adenine-treated animals showed
pale-colored kidneys. The color change was not distinct for
the kidneys of animals treated with sodium copper
chlorophyllin. Mild to moderate diffused foci were observed
in the disease control group which was reduced in the kidneys
of sodium copper chlorophyllin-treated animals. The adenine-
treated animals showed edematous kidneys as compared with
normal animals which were reduced with sodium copper
chlorophyllin treatment (Fig. 6).
Oxidative stress parameters
The malondialdehyde level was significantly increased (p <
0.001) adenine-treated animals when compared with normal
animals. Sodium copper chlorophyllin-treated animals
showed a significant reduction in MDA levels at dose 2.7
mg/kg (p < 0.05), 5.4 mg/kg (p < 0.01), and 10.8 mg/kg (p
< 0.001) wh en compared with disease control animals
(Table 2). The catalase, GSH, and SOD levels were signifi-
cantly decreased in adenine-treated animals. Sodium copper
chlorophyllin treatment significantly increased catalase, GSH,
and SOD levels at 10.8 mg/kg compared with the disease
control group (Table 2).
0.003
0.004
0.005
0.006
Normal Control
Disease Control
Cu- Chlorophyllin (2.7 mg/kg)
Cu - Chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg)
Cu -Chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg)
###
**
**
***
Treatment Groups
thgieWyendiKevitaleR%
Fig. 5 Effect of sodium copper
chlorophyllin on relative kidney
weight. All data are expressed as
mean ± SD (n = 10). The data was
analyzed using one-way ANOVA
followed by post hoc Dunnett’s
test. **p < 0.01, ***p <0.001
when compared with disease
control. ###p < 0.001 when com-
pared with normal control
Fig. 6 Overview of kidney tissues after sodium copper chlorophyllin
treatment. NC, normal control; DC, disease control; CD 2.7, sodium
copper chlorophyllin 2.7 mg/kg; CD 5.4, sodium copper chlorophyllin
5.4 mg/kg; and CD 10.8, sodium copper chlorophyllin 10.8 mg/kg
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol

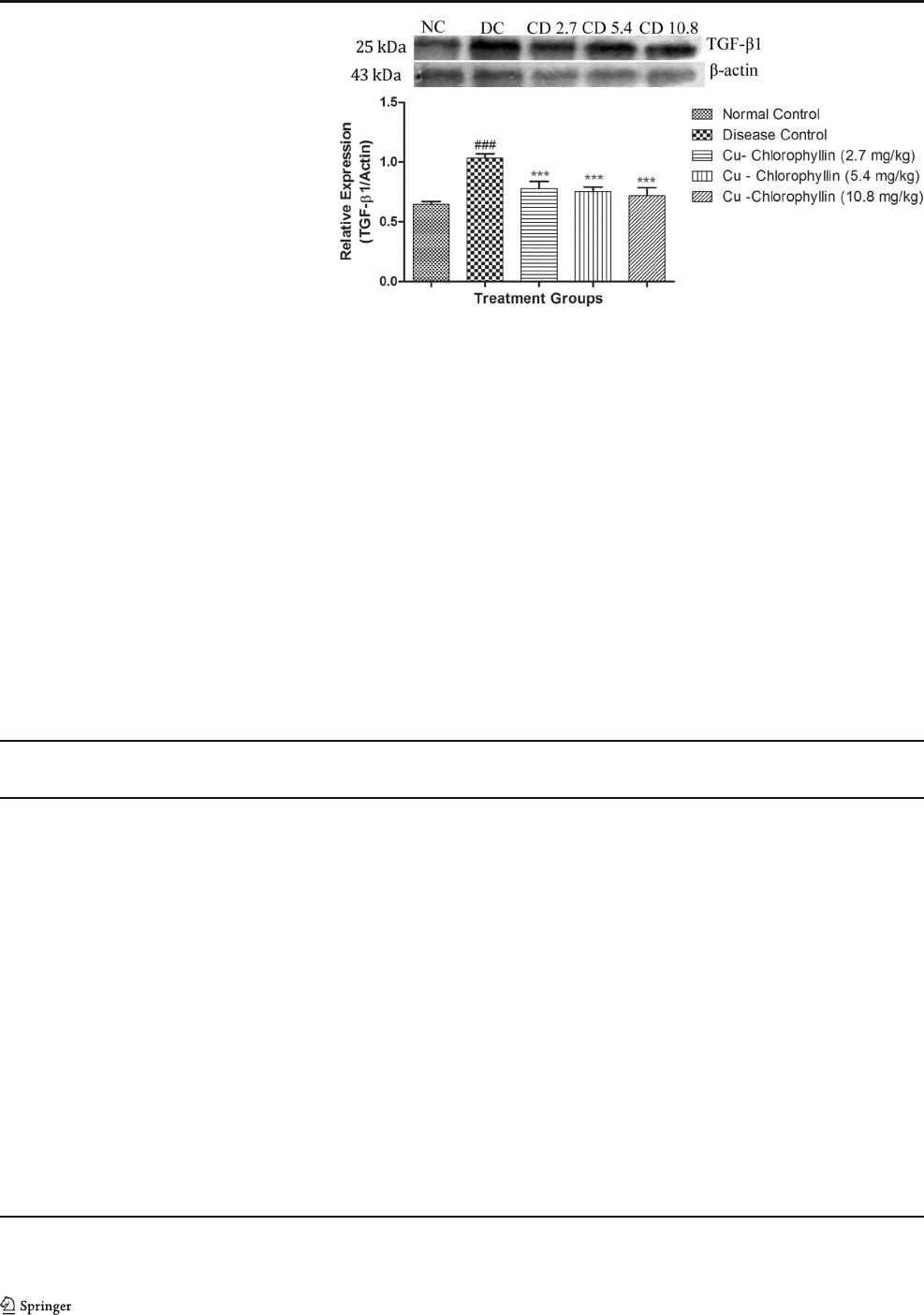
Western blotting
The TGF-β1 expression is responsible for basement mem-
brane thickening that leads to kidney hypertrophy and re-
duced glomerular filtration rate. Adenine-treated animals
showed increased expression of TGF-β1ascomparedwith
normal animals in kidney tissues. Sodium copper
chlorophyllin treatment significantly reduced (p <0.001)
relative TGF-β 1expressionwhencomparedwithadenine-
treated animals (Fig. 5 ).
Table 2 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin (SCC) on oxidative stress parameters in kidney tissue
Parameter Normal
control
Disease control Cu-
chlorophyllin
(2.7 mg/kg)
Cu-
chlorophyllin
(5.4 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(10.8 mg/kg)
MDA (nmol/mg protein) 2.02 ± 0.31 3.10 ± 0.78### 2.43 ± 0.53* 2.07 ± 0.42*** 2.00 ± 0.46***
Catalase (micromoles of H
2
O
2
decomposed/min/mg
protein)
0.009 ± 0.003 0.004 ±
0.002###
0.006 ± 0.002 0.007 ± 0.003* 0.008 ± 0.003**
GSH (micromole/mg protein) 3.53 ± 0.53 2.23 ± 0.52### 2.61 ± 0.53 2.95 ± 0.71* 3.05 ± 0.48**
SOD (U/mg protein) 0.130 ± 0.006 0.086 ±
0.003###
0.090 ± 0.002 0.100 ± 0.004 0.113 ±
0.006***
All data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 10). The data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’stest.*p <0.05,**p <0.01,
***p < 0.001 when compared with disease control. ###p < 0.001 when compared with normal control
Table 3 Histopathological examination of the kidneys (H&E staining)
Lesions Normal control Disease control Cu-chlorophyllin
(2.7 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(5.4 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(10.8 mg/kg)
Tubular dilation 0 3 2 1 1
Focal minimal 0 1 1 1 1
Focal mild 0 1 0 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 1 1 0 0
Tubular atrophy 0 4 2 2 2
Focal minimal 0 0 1 1 2
Focal mild 0 0 0 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 2 1 1 0
Multifocal moderate 0 2 0 0 0
Basement membrane thickening 0 3 1 0 0
Focal mild 0 2 1 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 1 0 0 0
Lymphocytic infiltration 0 4 3 2 2
Focal minimal 0 0 0 1 2
Focal mild 0 0 3 1 0
Multifocal mild 0 2 0 0 0
Multifocal moderate 0 2 0 0 0
Inter-tubular fibrosis 0 3 2 0 0
Focal minimal 0 1 1 0 0
Focal mild 0 1 0 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 1 1 0 0
Dilated Bowman’sspace 0 1 0 0 0
Focal mild 0 1 0 0 0
Giant cell infiltration 0 2 2 2 1
Focal minimal 0 2 2 2 1
Values indicate number of animals showing specific lesions (n =4)
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
Histopathology study
The treatment with sodium copper chlorophyllin improved
kidney histopathology when compared with the disease con-
trol group. The overview of kidney necropsy has been shown
in Fig. 6.
In H&E staining, microscopic examination of kidney
tissues of control anima ls did no t revea l any lesions of
pathological significance. The adenine-treated animals
showed various lesions in the kidneys such as focal mini-
mal to multifocal mild tubular, focal minimal to multifocal
moderate tubular atrophy, f ocal to multifocal mild thicken-
ing of the tubular basement membrane, focal minimal to
multifocal moderate lymphocytic infiltration, focal
minimal to multifocal mild inter-tubular fibrosis, focal
mild-dilated Bowman’ s space, and focal minimal giant cell
infiltration (Table 3). The microscopic observations of the
kidney suggested t hat disease control rats produced mini-
mal to moderate lesions. Treatment of sodium copper
chlorophyllin a t dose 2.7 mg/kg, 5.4 mg/kg, and 10.8
mg/kg reduced the severity and distribution of lesions in
the kidney (Fig. 7).
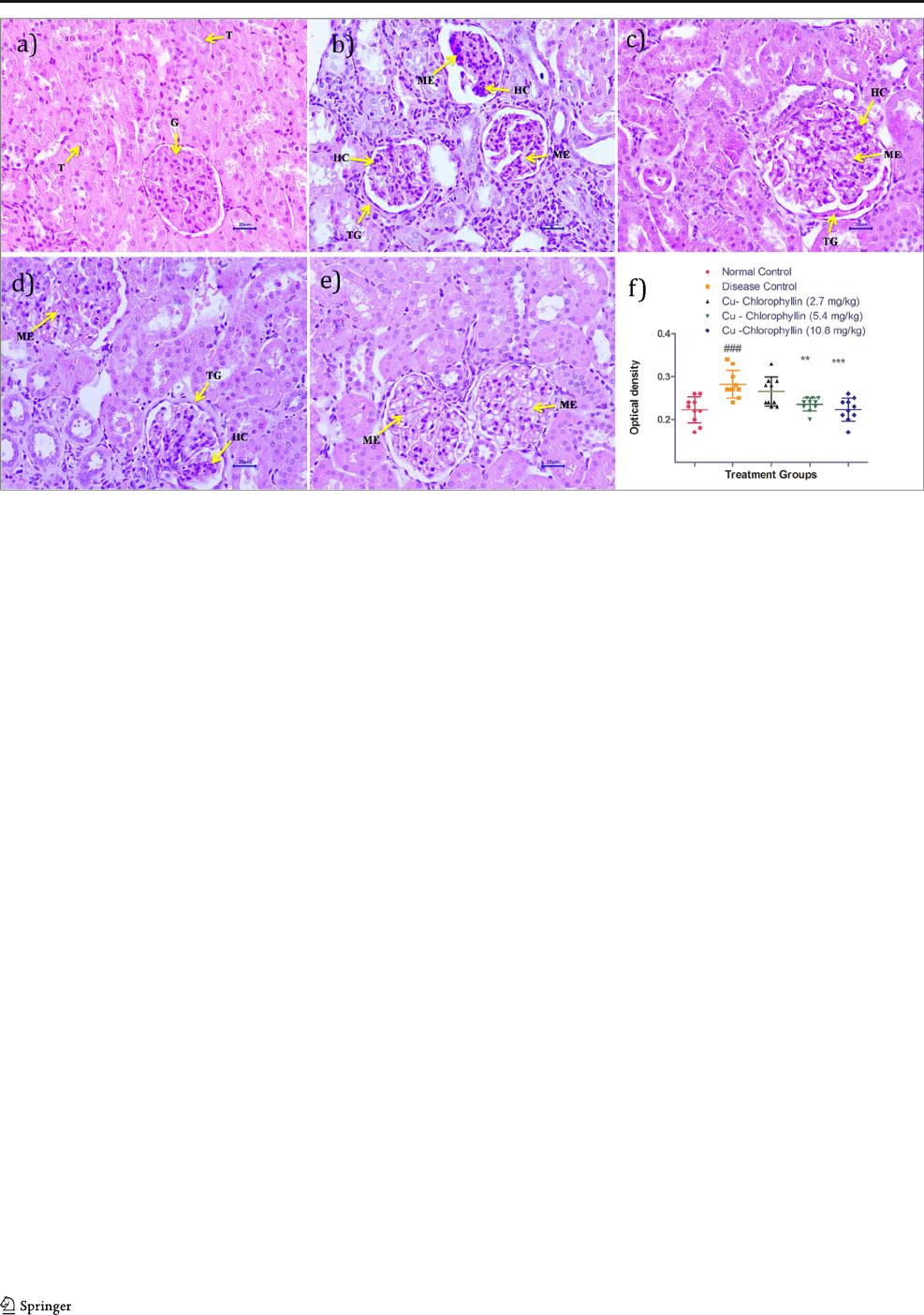
The PAS-stained kidney tissues showed multifocal
minimal to multifocal mild mesangial cell hypercellularity;
multifocal mild to diffuse moderate mesangial matrix expan-
sion; focal mild to multifocal moderate glomerular basement
membrane thickening in disease control animals as compared
with normal animals (Table 4). Sodium copper chlorophyllin
Fig. 7 Effect of sodium copper
chlorophyllin on the relative
expression of TGF-β1/actin by
Western blotting. All data are
expressed as mean ± SD (n =3).
The data was analyzed using one-
way ANOVA followed by post
hoc Dunnett’s test. ***p <0.001
when compared with disease
control. ###p < 0.001 when com-
pared with normal control
Table 4 Histopathological examination of the kidneys (PAS staining)
Lesions Normal control Disease control Cu-chlorophyllin
(2.7 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(5.4 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(10.8 mg/kg)
Mesangial matrix expansion 0 4 4 4 3
Focal minimal 0 0 0 0 1
Multifocal minimal 0 0 0 3 2
Multifocal mild 0 1 2 0 0
Multifocal moderate 0 1 0 0 0
Diffusemild 01110
Diffusemoderate 01100
Mesangial cell hypercellularity 0 4 3 3 3
Focal mild 0 0 0 0 2
Multifocal minimal 0 2 1 1 1
Multifocal mild 0 2 2 2 0
Thickening of glomerular basement membrane 0 4 4 3 1
Focal minimal 0 0 0 3 1
Focal mild 0 1 3 0 0
Multifocal minimal 0 0 1 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 2 0 0 0
Multifocal moderate 0 1 0 0 0
Values indicate number of animals showing specific lesions (n =4)
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
treatment reduced renal damage. Animals treated with sodium
copper chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg) showed a significant
reduction in mesangial expansion, leukocyte infiltration, and
glomerular basement thickening (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin on kidney tissue—H&E
staining (400X). a Normal control: showing normal histology, renal tu-
bule (small arrow), and glomeruli (large arrow). b disease control: show-
ing tubular dilation (star), tubular atrophy (large arrow), lymphocytic
infiltration (small arrow), thickening of the tubular basement membrane
(arrowhead), fibrosis (notched arrow). c Sodium copper chlorophyllin
(2.7 mg/kg): showing tubular dilation (arrowhead), tubular atrophy
(notched arrow), lymphocytic infiltration (large arrow), fibrosis (small
arrow). d Sodium copper chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg): showing tubular
dilation (arrowhead), lymphocytic infiltration (small arrow). e Sodium
copper chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg): showing lymphocytic infiltration
(small arrow)
Table 5 Histopathological examination of the kidneys (trichrome staining)
Lesions Normal control Disease control Cu-chlorophyllin
(2.7 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(5.4 mg/kg)
Cu-chlorophyllin
(10.8 mg/kg)
Tubular dilation 0 4 3 1 1
Focal minimal 0 0 2 1 1
Focal mild 0 2 0 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 2 1 0 0
Tubular atrophy 0 4 2 2 2
Focal minimal 0 0 1 1 1
Focal mild 0 0 1 0 1
Multifocal mild 0 3 0 1 0
Multifocal moderate 0 1 0 0 0
Deposition of ECM 0 4 1 1 0
Focal minimal 0 1 0 1 0
Multifocal minimal 0 1 1 0 0
Multifocal mild 0 2 0 0 0
Lymphocytic infiltration 0 4 3 4 0
Focal minimal 0 0 0 2 0
Focal mild 0 0 3 1 0
Multifocal mild 0 1 0 1 0
Multifocal moderate 0 3 0 0 0
Localization of collagen in glomeruli 0 4 4 4 2
Multifocal minimal 0 0 0 3 1
Multifocal mild 0 2 3 1 1
Multifocal moderate 0 2 1 0 0
Increased deposition of collagen in inter-tubular space and renal
capsule
04443
Focal minimal 0 0 1 2 1
Focal mild 0 0 1 2 2
Multifocal mild 0 1 2 0 0
Multifocal moderate 0 2 0 0 0
Multifocal marked 0 1 0 0 0
Values indicate number of animals showing specific lesions (n =4)
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
Trichrome-stained kidney tissues showed increased colla-
gen deposition in inter-tubular spaces and in renal capsules in
the adenine-treated group. Addit ionally, various treatment
groups showed focal minimal to multifocal mild tubular dila-
tion, focal minimal to multifocal moderate tubular atrophy,
focal minimal to multifocal mild deposition of extracellular
matrix (ECM), multifocal minimal to moderate localization
of colla gen in gl omeruli, and focal mi nimal to multifoca l
marked increased deposition of collagen in inter-tubular space
and renal capsule (Table 5). The collagen deposition in the
inter-tubular spaces, renal capsules, and glomeruli was de-
creased with sodium copper chlorophyllin treatment as com-
pared with the disease control group. The sodium copper
chlorophyllin treatment also significantly reduced the lym-
phocytic infiltration and ECM deposition in the kidneys when
compared with the disease control group (Figs. 9 and 10).
Discussion
Sodium copper chlorophyllin is a non-toxic, semi-synthetic
derivative of plant pigment. Sodium copper chlorophyllin is
more hydrophilic and more stable to the light and acid as
compared with natural chlorophyll (Tumolo and Lanfer-
Marquez 2012). It is an approved colorant and food additive
in various countries; it is a bioactive compound with antioxi-
dant, anti-mutagenic, anti-apoptotic, and immunomodulatory
properties (Lai et al. 1980;Satoetal.1984; Chu et al. 2002).
Hence, the study was designed to evaluate the effect of sodium
copper chlorophyllin on chronic kidney disease.
Chronic kidney disease causes severe kidney damage
which is characterized by increased plasma creatinine, potas-
sium, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and BUN, and decreased
urea clearance, creatinine clearance, plasma proteins, and al-
bumin levels (Shuvy et al. 2011). It has been reported that
kidney damage alters body weight, food, and water intake
(Diwan et al. 2017, 2018). Adenine intake reduces the body
weight and food intake and increases water intake probably by
interfering with liver enzymes like CYP450 and metabolic
process (Yokozawa et al. 2005). Sodium copper chlorophyllin
treatment significantly improved food, water intake and body
weight. Sodium copper chlorophyllin treatment also signifi-
cantly reduced kidney hypertrophy
CKD is clinically diagnosed by analysis of biochemical
and urine parameters like albuminuria, proteinuria and hema-
turia; decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR); and finally
renal failure. Biochemical parameters are significantly altered
into chronic kidney disease due to remarkable kidney damage.
Fig. 9 Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin on kidney tissues—PAS
staining (400X). a Normal control: showing normal histology, renal tu-
bule (T) and glomeruli (G). b Disease control: showing mesangial matrix
expansion (ME), mesangial cell hypercellularity (HC), thickened glomer-
ular basement membrane (TG). c Sodium copper chlor ophyllin (2.7
mg/kg): showing mesangial matrix expansion (ME), mesangial cell
hypercellularity (HC), thickened glomerular basement membrane (TG).
d Sodium copper chlorophyllin (5.4 mg/kg): showing mesangial matrix
expansion (ME), thickened glomerular basement membrane (TG). e
Sodium copper chlorophyllin (10.8 mg/kg): showing mesangial matrix
expansion (ME). f Histogram of PAS staining. All data are expressed as
mean ± SD. The data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by
post hoc Dunnett’stest.**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared with
disease control. ###p < 0.001 when compared with normal control
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol
