Mutual Authentication Based on HECC
for RFID Implant Systems
Asha Liza John
(&)
and Sabu M. Thampi
Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management - Kerala (IIITM-K),
Technopark Campus, Trivandrum, India
{asha.mphilcs3,sabu.thampi}@iiitmk.ac.in
Abstract. The Internet of Things (IoT) is an environment in which “things”
(objects, animals or people) are provided with unique identifiers (IPv6 addres-
ses) and the ability to communicate over a network without requiring
human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. Radio-Frequency Identifi-
cation Technology (RFID) is the key enabler of the IoT. The RFID Implant
System considered in the proposed work consists of an implantable, passive
RFID tag which is a data carrying device that is attached to the object to be
identified, RFID reader which communicates with the tag in order to read or
write data to its memory and, the back-end database which stores information
related to the identified object. There are several security issues associated with
the use of RFID tags in IoT like eavesdropping, impersonation, cloning, replay
attack, tag destruction, unauthorized tag reading, tag modification etc. To defend
such attacks effectively, efficient security mechanisms are essential. So, the
proposed system aims to provide a secure mutual authentication mechanism
based on Hyper Elliptic Curve Cryptography (HECC) to authenticate the
communication between the RFID tag and reader. The security of Hyper-elliptic
Curve Cryptosystem depends on the hardness of solving hyper-elliptic curve
discrete logarithm problem (HCDLP). This problem helps to avoid the eaves-
dropper from breaking into the security of the HECC cryptosystem. The pro-
posed work also uses D-Quark hash algorithm.
Keywords: RFID Implant System
IoT Security Healthcare Mutual
authentication
Hyper-elliptic curve cryptography
1 Introduction
Internet of Things (IoT) involves the concept of connecting everything around, to the
internet. These things may include wearable devices, metering devices, environmental
sensors etc. As a result of this, in the near future, there may be trillions of connected
devices which may communicate with each other by exchanging data. This commu-
nication between devices is made possi ble via wireless networks. Wireless networks use
radio communication frequencies and follows radio regulations. Hence, Radio Fre-
quency Identification (RFID) is the key enabler of IoT. IoT along with RFID technology
has many applications in smart home, healthcare system, inventory management etc.
© Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2016
P. Mueller et al. (Eds.): SSCC 2016, CCIS 625, pp. 18–29, 2016.
DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-2738-3_2
Providing health care was far simpler than it is today. But, advent of legislation,
technology and reimbursement charges has forced the entire healthcare system to shift
the way care is provided. However, there are opportunities to improve patient expe-
rience. Historically, physicians did not have access to a holistic view of the patients’
health so they were forced to make treatment decisions, with limited or partial data.
Soon the trend shifted from this to Electronic Medical Records (EMR) by which it is
possible to collect complete medical records of a patient. When data from such EMR
systems and consumer wearables are merged, it is possible to organize and process data
beyond typical clinical scenarios. At the same time, advances in technology provided
new and low cost ways to detect diseases. When all these combine, the pa tients and
physicians benefit from more comprehensive views of patient health and treatment
progress enabling physicians to more accurately adjust treatments. Hospitals may not
have the resources to monitor everyone and people with such resources cannot monitor
themselves. Meanwhile, funding constraints depend on optimization solutions to
effectively and efficiently distribute and manage equipment. So, facilities need to rely
on pervasive technologies like passive RFID tags to supplement monitoring and
management efforts.
The RFID Implant System mentioned in the proposed work is a resource con-
strained system which has three main compo nents – Implantable RFID tag which is a
passive tag (almost the size of a rice grain) implanted into the patient’s body, RFID
Reader which communicates with both the tag and the back-en d server, and a Back-end
server which stores the information about the patient. The communication channel
between the reader and the back end server is secure. But, the wireless communication
channel between the reader and the tag is found to be insecure and hence, may be
vulnerable to attacks like unauthorize d location tracking, eavesdropping attack,
impersonation attack, replay attack etc. Hence, both the tag and the reader must be
assured that the other end is legitimate. In the healthcare scenario, providing robust and
secure data communication is crucial so, the authentication of tag by reader is just not
enough because the information about a particular patient, which the tag shares with the
reader, is highly sensiti ve. So before sharing such sensitive data, the tag must make
sure that the reader is legitimate. For this, a two way authentication or mutual
authentication mechanism between the tag and the reader is essential. Hence in this
work, we propose a mutual authentication mechanism to authenticate the communi-
cation between, RFID Reader and the RFID Tag.
As mentioned before, RFID Implant System is a resource constrained system since,
the implanted RFID tag has only very less processing power. Hence, it requires efficient
and optimized security solutions. The mutual authentication based on elliptic curve
cryptography (ECC) or non-ECC mechanisms so far implemented for RFID systems in
general are not adequately optimized to operate in resource constrained environments.
So, in this work, we combine the concepts of Hyper-elliptic curves (HECC) and
D-Quark hash algorithm to formulate an optimized and efficient mechanism for mutual
authentication of RFID Reader and Tag.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Sect. 2 provides an overview
of related work and literature. Section 3 presents the proposed HECC-based mutual
authentication scheme for the RFID implant systems. Section 4 provides a co mpre-
hensive security and computational performance analysis of our scheme. In this
Mutual Authentication Based on HECC for RFID Implant Systems 19
section, the comparison of this work with similar existing approaches is also presented.
Finally, Sect. 5 concludes and summarizes the work.
2 Related Works
Currently there are several security and privacy concerns which restrict the use of
implantable tags. Mitrokotsa, Rieback and Tanenbaum class ifies these RFID attacks
based on its layer of operation [6]. Among these, the most popular attacks are the ones
affecting network layer. The attacks on Network-Transport layer are classified into tag
attacks and reader attacks. Attacks on tags are cloning, spoofing and many more and
that on reader are impersonation, eavesdropping etc. There are several existing security
mechanisms to defend these attacks. But this section, revie ws only those literature
dealing with authentication since the proposed system attempts to develop a mutual
authentication mechanism.
Authentication can be ensured by generation and verification of digital signatures
by both the communicating parties. In their paper Radu-Ioan Paise and Serge Vaudenay
emphasizes the importance of mutual authentication [8]. A malicious reader can obtain
unauthorized information from a tag, raising security or privacy issues. In order to fix
this problem, besides tag’s authentication, a protocol must ensure reader’s authenti-
cation. To ensure this, a mutual authen tication protocol is used. So far, several mutual
authentication techniques have been proposed based on cryptographic algorithms like
IDEA [2], AES [9], ECC [3]. Among these, algorithms based on elliptic curve cryp-
tography are considered more suitable for application in constrained devices, because
ECC uses shorter keys which results in faster execution and less memory utilization.
In 2006, Tuyls et al. proposed an ECC-based RFID identification scheme based on
Schnorr identification protocol [10]. But, in 2008 Lee et al. found out that this iden-
tification scheme is vulnerable to location tracking attack and that it does not ensure
forward security [5]. In 2007, Batina et al. proposed an ECC-based RFID identification
scheme based on Okamoto’s authentication algorithm [1]. But in 2008, Lee et al.
proved that like Tuyls et al. scheme, this scheme is also prone to tracking and forward
secrecy problem [5]. Hence, Lee et al. in 2010, proposed an ECC based RFID
authentication scheme so as to solve the existing tracking problems [4]. Again, in 2011,
Zhang et al. proposed an ECC-based randomized key scheme in order to improve Tuyls
et al.’s and Lee et al.’s schemes [12]. This scheme defended almost all relevant attacks
concerning the RFID systems. But, in all these schemes, the authors merely considered
one-way authentication of tag by reader, excluding the possibility of authentication of
reader by tag. This causes tags to reply to any malicious query being sent by an
adversary. In 2013 , Liao et al. proposed a secure ECC-based authentication scheme
integrated with ID-verifier transfer protocol. But, the tag identification scheme suffered
from lack of performance efficiency in terms of the tag’s computation time and memory
requirement [13]. Moosa vi, Nigussie and Isoaho implemented a mutual authentication
scheme based on the concept of Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) on RFID Implant
Systems [7]. But in 2014 Barsgade et al. compared elliptic curve curves and hyper
elliptic curves in DLP and found that HECC is as good as ECC with less computational
complexity [11] (Table 1).
20 A.L. John and S.M. Thampi
From the research conducted on existing security mechanisms it is found that
conventional security and protection mechanisms are not adequate for RFID Implant
Systems since it is resource constrained. So, RFID implant system still requires a
robust, optimi zed, and ligh tweight security framework. So in the proposed system we
combined concepts and algorithms with less power and memory requirements like
HECC, D-Quark lightweight hash algorithm and Harley’s algorithm for divisor com-
putation to develop an optimized and efficient mutual authentication mechanism to
ensure authentication between the implanted RFID tag and the RFID reader in a
resource constrained RFID Implant System.
3 Proposed Authentication Mechanism
Mutual Authentication can be ensured via generation and verification of digital sig-
natures by both the communicating parties. Hence the proposed algorithm for mutual
authentication is imp lemented with reference to Digital Signature Algorithm in Digital
Signature Standard published in Federal Information Processing Standards Publications
(FIPS PUBS 186) which are issued by the National Institute of Standards and Tech-
nology (NIST). This standard specifies that a Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) is
appropriate for all applications requiring a digital signature. It is assumed that the
reader side has a list of valid tag IDs and the tag side has a list of valid reader IDs. The
proposed method is a two stage process. On entering the radio frequency field of the
RFID reader, the passive implanted RFID tag, gets activated, and sends its ID to the
reader. The reader checks with the database to see if this ID is already present in the
list. If so, then the reader sends its ID to the tag. Further, a similar checking happens at
the tag side. If b oth IDs are found to be valid, then mutually authenticated commu-
nication begins. The proposed algorithm has three modules (or phases ):
1. Generation of Global Public Parameters and Key Generation
2. Signature Generation
3. Signature Verification
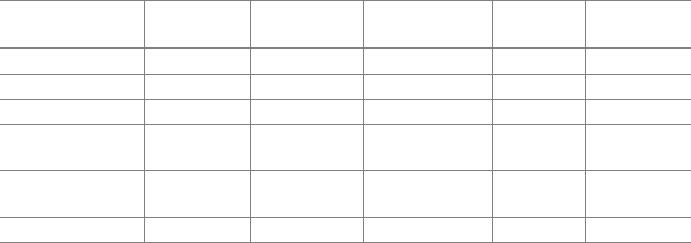
Table 1. Comparison of existing schemes
Batina
et al. [1]
Zhang
et al. [12]
Liao and
Hsiao [13]
Lee
et al. [5]
Moosavi
et al. [7]
Eavesdropping Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Impersonation No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Replay attack Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Forward
security
No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Mutual
authentication
No No Yes No Yes
Performance Less Less Less Less Better
Mutual Authentication Based on HECC for RFID Implant Systems 21
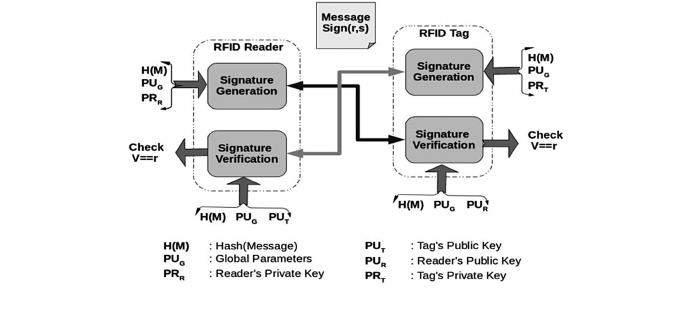
Figure 1 illustrates the proposed method of mutual authentication developed with
reference to existing standard DSA. Each of the modules are explained in detail in the
following subsections.
3.1 Generation of Global Public Parameters
Signature generation requires the use of some global parameters which are publicly
available. In DSA, there are three global parameters. But in the proposed work, the
global parameters introduced are all based on the concept of Hyper-elliptic curve
cryptography. This is because; solving the Discrete Logarithm Problem of an 80-bit
Hyper-elliptic Curve is as hard as that of a 160-bit Elliptic-curve. So, Hyper-elliptic
curves are more suitable for resource constrained systems like RFID Implant System.
The chosen global parameters are finite prime field Fp, Hyper elliptic curve C of genus
2 over prime field Fp, Unique Reduced Divisor D over Hyper elliptic curve C, a large
random number p, large prime divisor q of p-1. The unique reduced divisor D over
hyper elliptic curve C can be computed using either Harley’s Algorithm or Cantor’s
Algorithm. Divisor D will be represented in Mumford form as <u, v>.
After generation of global parameters, the next step is to generate the public and
private keys required for the signing and verification process at both ends. Signature
generation requires the use of private key for signing the message and signature ver-
ification uses public key of the corresponding party for verification of the signed
message. Private Key PR is a random number such that PR < q and public key PU is
computed using the private key as PU = PR∗D’ where parameter D’ =u+v.
3.2 Signature Generation
In the proposed algorithm, the signature generation takes as input a message M and
generates a signature pair (r, s) as output. Further the generated signature pair (r, s) is
appended to the message to be transmitted to the receiver as (M, r, s) and is then send to
Fig. 1. Block diagram of proposed system
22 A.L. John and S.M. Thampi
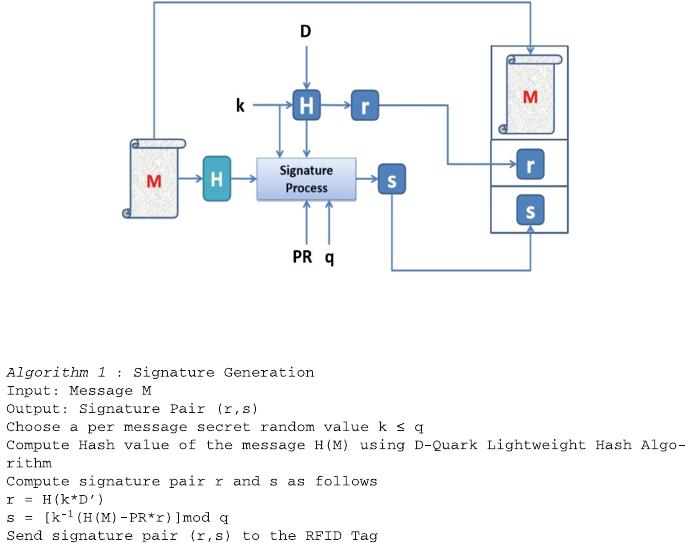
the receiver side. Although the overall process is similar to that in DSA, the compu-
tation of signature pair (r, s) is different in the proposed signature generation algorithm.
Figure 2 shown below, illustrates the signing process. Algorithm 1 shown below
explains the computation.
Here, the per-message secret random value k is newly generated each time a
message is send and is destroyed and never reused. The message M as such is not used
for calculating the signature pairs. Instead, the hash value of the message is calculated
using a lightweight hash algorithm in the Quark series called the D-Quark Hash
algorithm. Although, DSS Standard speci fies the use of Secure Hash Algorithm
(SHA-1), we use D-Quark because, hash value calculation using SHA algorithm is
computationally intensive. D-Quark consumes less power and memory compared to
SHA-1. Further, the signature pair (r, s) is calculated as shown in the algorithm.
3.3 Signature Verification
Signature verification takes as input the received message and signature pair (M’,r’,s’)
and compu tes four new parameters w, u1, u2 and V out of which, the value of V must
be equal to r for the signature to be valid. As in the case of signature generation, the
Fig. 2. Signature generation
Mutual Authentication Based on HECC for RFID Implant Systems 23
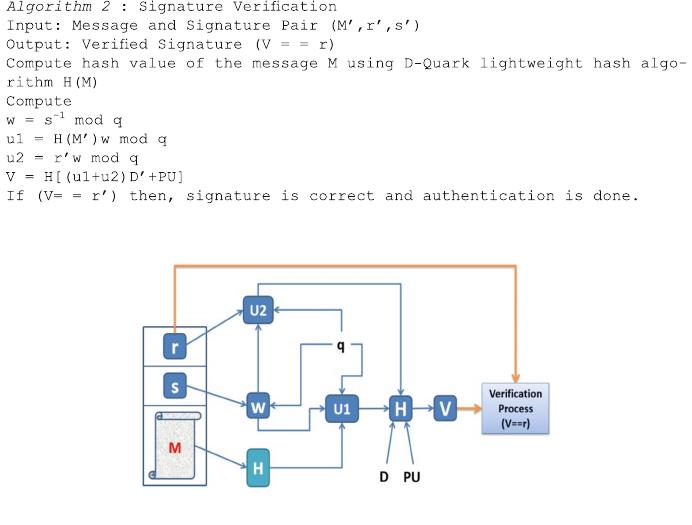
signature verification process is also similar to that of DSA but, the formulae for
computing V value is different. The computation of parameters w, u1, u2 and V are
explained in Algorithm 3 described below. Figure 3 illustrates the whole process of
verification.
The verification process mentioned in Algorithm 2 uses public key PU for verifi-
cation. Both signature generation and signature verification algorithms should be
implemented in both the RFID Reader as well as RFID tag side since the aim of the
proposed work is to ensure mutual authentication. This is illustrated in the block
diagram shown in Fig. 1.
3.4 Proof of V = = r
As mentioned before, for the proposed mutual authentication mechanism to be valid,
the parameter V calculated during the signature verification phase must be equal to the
signature value r. The statements below prove the credi bility of this argument
mathematically.
Fig. 3. Signature verification
24 A.L. John and S.M. Thampi
V ¼ H½ðu1 þ u2ÞD
0
þ PU as per proposed algorithm
¼ H½ðu1 D
0
Þþðu2 D
0
ÞþPR D
0
ðDistributive property a nd PU ¼ PR D
0
Þ
¼ H[ðu1 þ u2 þ PR ÞD
0
ðDistributive propertyÞ
¼ H½½HðMÞw mod q þ r w mod q þ PR D
0
ðas per equations of u1 and u2Þ
¼ H[½HðMÞw mod q þ r w mod q þ PR mod q D
0
since PR\qPR¼ PR mod q
¼ H[½HðMÞw mod q þ r w PR mod qD
0
¼ H½½ðHðMÞþPR rÞ w mod qD
0
¼ H½½ðk s wÞ mod q D
0
as per calculation of s
¼ H½½ðk s s 1Þ mod qD
0
as per calculation of w
¼ H½½k mod q D
0
¼ H½k D
0
since k\q
¼ r
4 Security and Performance Analysis
This section, analyses the security and performance of the proposed scheme in order to
verify whether the essential requirements have been satisfied.
4.1 Security Analysis
Security of the proposed mutual authentication mechanism depends on the difficulty of
solving the Hyper- elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem (HCDLP). Analyses of
the proposed scheme against some of the relevant attacks are as follows:
• Mutual Authentication is achieved in this scheme by following DSA standard.
• Availability of the system is affected by DoS attacks. But this type of attack is
possible only if adversary knows the per message secret value k. But this is
impossible since the r value is hashed using D-Quark, before being transmitted to
the receiving end. So, availability is ensured.
• Forward Security is ensured by destroying the per-message secret key k after
sending each message.
• Unauthorized Tracking is not possible, since each communication between the
reader and the tag are mutually authenticated.
• Replay attack is not possible since the p er message secret key k is involved in each
communication. Also, the key changes after each message
4.2 Performance Analysis
The performance of the proposed algorithm is influenced by three major factors - Hyper
elliptic Curves, D-Quark Hash Algorithm and Harley’s algorithm for computing unique
Mutual Authentication Based on HECC for RFID Implant Systems 25
reduced divisor. From theoretical analysis it can be proved that the hardness of solving
an 80 bit HCDLP is equal to the hardness of solving a 160 bit ECDLP. Hence the use
of hyper elliptic curves instead of elliptic curves in the proposed work improves the
performance. Also, the use of D-Quark lightweight hashing mechanism also improved
the computational efficiency of the proposed mutual authentication algorithm. The third
factor which influenced the computation is Harley’s algorithm. Usually, the algorithm
used for divisor computation is Cantor’s algorithm which is a generic algorithm that
involves polynomial arithmetic computation. But Harley’s algorithm converts poly-
nomial arithmetic to field arithmetic and thereby decreasing the time and cost of
computation. But, there are still a negli gible number of exceptional cases in which
Harley’s algorithm cannot find a divisor. For such cases alone, Cantor’s algorithm is
used.
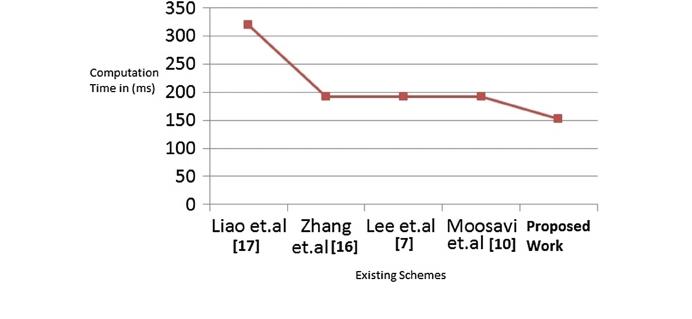
Figure 4 shows the performance graph of the proposed scheme in comparison with
the existing schemes. From the graph, it is found that the computation time of the
proposed hyper elliptic curve based mutual authentication algorithm is less than that of
all the existing schemes based on elliptic curve cryptography. This is because of
reduced key-size, use of lightweight D-Quark hash algorithm and use of Harley’s
algorithm for calculating the divisor of the hyper elliptic curve.
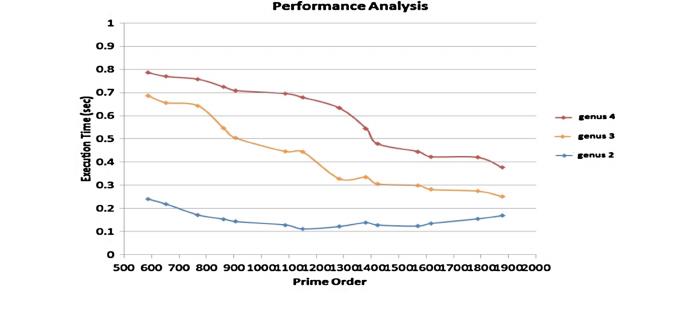
Figure 5 shows the results of the simulation of the proposed mutual authentication
algorithm in Python using a package called Sage-Math. The simulation was done for
genus values 2, 3 and 4 and over a range of field order values. From the graph it is
evident that execution time for genus 2 hyper-elliptic curves is much less than genus 3
and genus 4 curves and its execution time approaches the genus 3 and genus 4 curves
for higher prime order values. Also, it is proven that genus 2 curves are more secure
compared to the other two curves of genus 3 and 4. [14] Hence, in the proposed work
we chose hyper elliptic curves of genus 2.
Fig. 4. Comparison with existing schemes
26 A.L. John and S.M. Thampi
4.3 Comparison with ECC Based Signature and Verification Mechanism
The effort required by the best algorithms to solve the Discrete Logarithm Problem, in
worst case, is O(√|G|) group operations. For curves of genus g over a finite field F
q
,
|G| ≈ q
g
as q → ∞. The minimum level of security recommended is 80 bits. i.e.
√(q
g
) ≈ 2
80
. Elliptic curves are hyper elliptic curves of genus g = 1. Therefore, the
number of group operations required to solve ECDLP is |G| = q
1
≈ 2
160
. From this we
find that value of q = 2
160
. For the proposed scheme, we use hyper-elliptic curves of
genus g = 2. Therefore, number of group operations required to solve HCDLP is same
as that required for ECDLP which is |G| = q
2
≈ 2
160
. But for hyper-elliptic curves the
value of q reduces to q = 2
80
. Hence, from the above analysis it is evident that the
hardness of solving an 80 bit HCDLP is equal to the hardness of solving a 160 bit
ECDLP. Thus, shifting the focus from elliptic curves to hyper elliptic curves reduces
key size which in turn leads to easier data management, minimum hardware and
bandwidth requirement, increased battery life etc.
ECC based signature and verification mechanism uses SHA-1 for hashing. But
SHA-1 is proved to be vulnerable and is not a lightweight hash algorithm. So in the
proposed scheme we replaced SHA-1 with a light weight hashing mechanism called
D-Quark. This consumes less power for execution and also provides more security
since it has more number of rounds.
In ECC based signature and verification mechanism the coordinates of the points on
the curve are directly employed for calculation. But, in the case of hyper-elliptic curves
the divisor calculation is done using Harley’s and Cantor’s algorithm. Hence, the
proposed scheme based on HECC performs better than the existing ECC based sig-
nature and verification schemes.
Fig. 5. Results of simulation
Mutual Authentication Based on HECC for RFID Implant Systems 27
