High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 2008; 15 (3): 171-215
C
ONTRIBUTIONS FROM
I
NTERNATIONAL
C
ONGRESS
1120-9879/08/0003-0171/$48.00/0
© 2008 Adis Data Information BV. All rights reserved.
Heart
5.13 Arterial Hypertension and Hyperhomocysteinaemia with TT
Polymorphism of the C677T Gene for the 5-10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
Reductase: Risk Factors able to influence Clinical Management of the
Patent Foramen Ovale?
A. Mazza (1), S. Zamboni (1), S. Cuppini (1), M. Armigliato (1), P. Rempelou (2),
A. Camerotto (3), M. Gusella (4), A.C. Pessina (2), V. Tikhonoff (2), E. Casiglia (2)
(1)SOC di Medicina Interna - Azienda ULSS 18 Rovigo, Rovigo; (2)Dipartimento
di Medicina Clinica e Sperimentale, Universit
`
a degli Studi di Padova, Padova;
(3)Servizio di Medicina di Laboratorio - Ospedale San Luca, Trecenta; (4)SOC di
Oncologia Medica - Azienda ULSS 18, Rovigo, Italy
Introduction. In subjects aged <55 years, the association between patent foramen ovale (PFO) and
cryptogenetic cerebrovascular (CV) events is well established. In the clinical management of the PFO,
a thrombophilic screening including homocysteinaemia (Hcy) determination and methylenete-
trahydrofolate reductase polymorphism (MTHFR) evaluation for the C677T gene are recommended.
Methods. One hundred and three hypertensive subjects (blood pressure >140/90mmHg or under anti-
hypertensive treatment), of which 63 men and 40 women (aged 49.8± 11.3 years) with hyper-Hcy (i.e.
>14μg/dL) referring to our Hypertension Centre, undergo a trans-thoracic echocardiogram (Eco-T)
and evaluation of MTHFR polymorphism (CC, CT, TT) for the C677T gene mutation. Continuous
variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation; analysis of variance was used to comparing
groups, and Pearson chi square ^2 test to compare the prevalence of categorical variables.
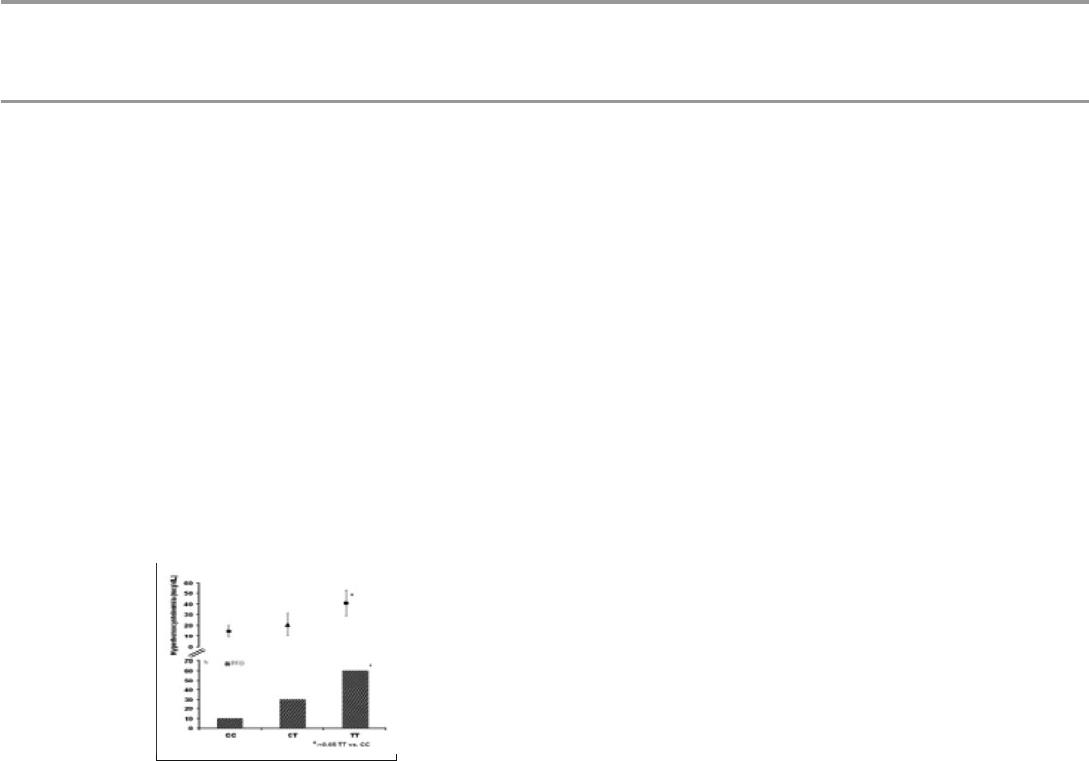
Results. Eighteen mutated cases were found (10 TT and 8 CT). Eco-T discovered 10 cases (7 men and
3 women) of unknown PFO with a left-right shunt (subsequently confirmed by trans-oesophageal
echocardiography). PFO prevalence was significantly higher in TT than CT and CC subjects (see
figure); in subjects with PFO, Hcy was significantly increased in TT than in CC subjects (see figure 1);
no difference both systolic and diastolic blood pressure was found in TT than in CC (166. 4±1.4 vs
159.8± 14.6 mmHg and 94.4±4.2 vs 92.8± 3.0 mmHg, respectively).
Conclusions. Although PFO prevalence at population level was around of 25%, in the hypertensive
subject it would seem to associate with hyper-Hcy and homozygosis for MTHFR 677. Currently no
randomized clinical studies are available for the PFO management in subjects having hyper-Hcy and
homozygosis for MTHFR. In this subjects hypertension increase per se the global CV risk, putting a
question if the endo-vascular treatment of PFO must be performed independently from its entity.
